In this article, we will learn the step-by-step process to make a safe and secure WordPress website with GoDaddy hosting.
Points to learn:
- How to check a domain name for any trademark infringement?
- Which of GoDaddy’s WordPress plans to purchase based on your website’s needs?
- How to add an existing domain name to your WordPress website?
- How to get a Free SSL Certificate?
- How to create and customize your website?
- Which plugins to install?
- How to make your website responsive for tablet and mobile devices?
1. Brainstorm Domain Name Ideas
What is a domain name?
The domain name is the name of a website plus the extension that visitors type into the search bar to reach a website. For instance, the domain name for the company Apple is “apple.com.” In this example, “apple” is the name and “.com” is the extension. Together, they form a domain name. Apart from the “.com” extension, there are a variety of other extensions that websites use in their domain names, such as:
- .”net”: suitable for tech companies.
- “.org”: suitable for non-profit organizations, open-source projects, and communities.
- “.edu”: suitable for educational websites.
- “.gov”: suitable for government websites.
- “.biz”: suitable for business websites.
- “.info”: suitable for information sharing websites.
- “.tv”: suitable for video streaming websites.
- “.store”: suitable for e-commerce stores.
- Location-specific extensions, such as “.ca” for Canada, “.uk” for the UK, and “.eu” for the European Union suitable for serving a specific country or region.
Does the Domain Extension Matter?
Yes, the domain extension matters to some extent. It is worth noting here that the “.com” extension is the most popular domain extension. It is generally suitable for any type of website, unless it is a government website. A website with the “.com” extension is easy to recall and looks more credible. The domain names with the “.com” extension are trusted more because it is the oldest and most widely used extension, and people have now become used to it. Without a doubt, it is the most widely recognized extension with a high trust score. Therefore, you should aim for the “.com” extension unless you have a specific need to convey the nature or location of your business.
Choosing a Domain Name
The first step to creating any website is to come up with a suitable domain name. The domain name should reflect the nature of your business and the purpose of your website. This step requires some time and effort because internet is an old space now and many desirable domain names are already taken.
A creative and catchy website name can do a little bit of marketing for your business right from the beginning. For instance, there is a famous travel blog named “Anywhere We Roam.” The title exquisitely conveys the idea that the blog is about travel in a casual tone. Coming up with a unique and creative domain name idea is a good marketing strategy. You can also take assistance from online domain name generators to search for potential domain name ideas. Additionally, to check whether a domain name is available or not, you can use the GoDaddy domain name generator.
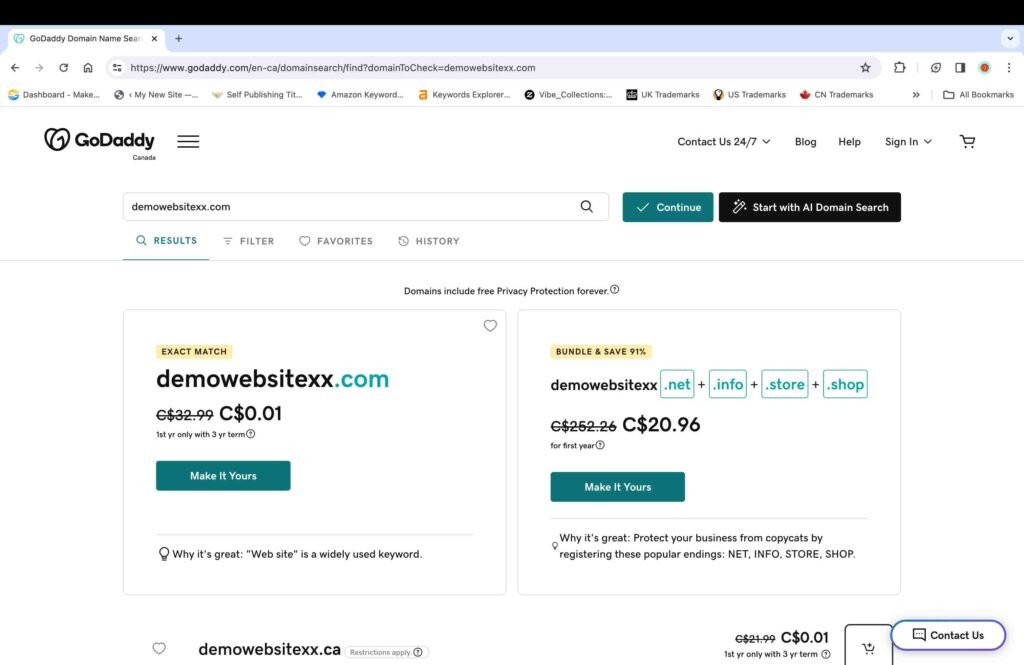
2. Check for any Trademark Infringements
Even if a domain name is available, that does not mean it is free to use. You should always check the trademark database, both domestically and internationally, to make sure that the domain name is not already trademarked by any business. You should perform the following steps to thoroughly check for any trademark infringement:
A. Domestic Trademark Search
- Search the official trademark database of your country to check for any trademark infringements.
- For instance, the official trademark website for the US is UPSTO. If you are located in the US, you should look up domestic trademark records in UPSTO to make sure that the domain name is safe to use in your home country.
B. International Trademark Search
- Perform a search in the Global Brand Database of the WIPO, which provides an international trademark database across multiple countries.
It is advisable to stay away from trademarked names to avoid any legal challenges in the future.
3. Purchase a Web Hosting Plan
GoDaddy offers two types of website hosting:
- Web Hosting can host any type of website.
- WordPress Hosting is specifically optimized for WordPress websites, such as backups, malware scans, and firewalls.
WordPress hosting plans are more expensive than web hosting plans because of the additional features offered.
There are two types of web hosting plans:
- Standard Performance Plans: These are ideal for simple and basic websites with minimal resource usage.
- High Performance Plans: These are ideal for high-traffic and resource-heavy websites.
The maximum number of websites that you can host and the storage space offered will vary from plan to plan.
For the purpose of this tutorial, the Web Hosting Economy Plan was chosen.
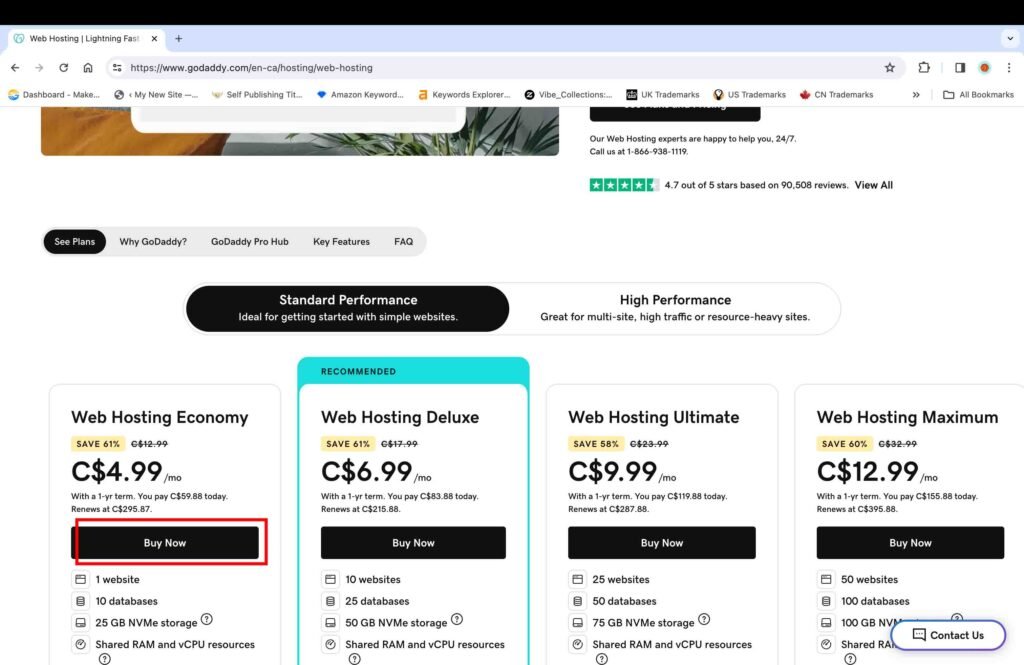
- Click the “Buy Now” button.
- Select the desired period of the plan.
- Click the “Continue to Cart” button.

- Create an account with any of the three options provided: Facebook, Google, or e-mail.
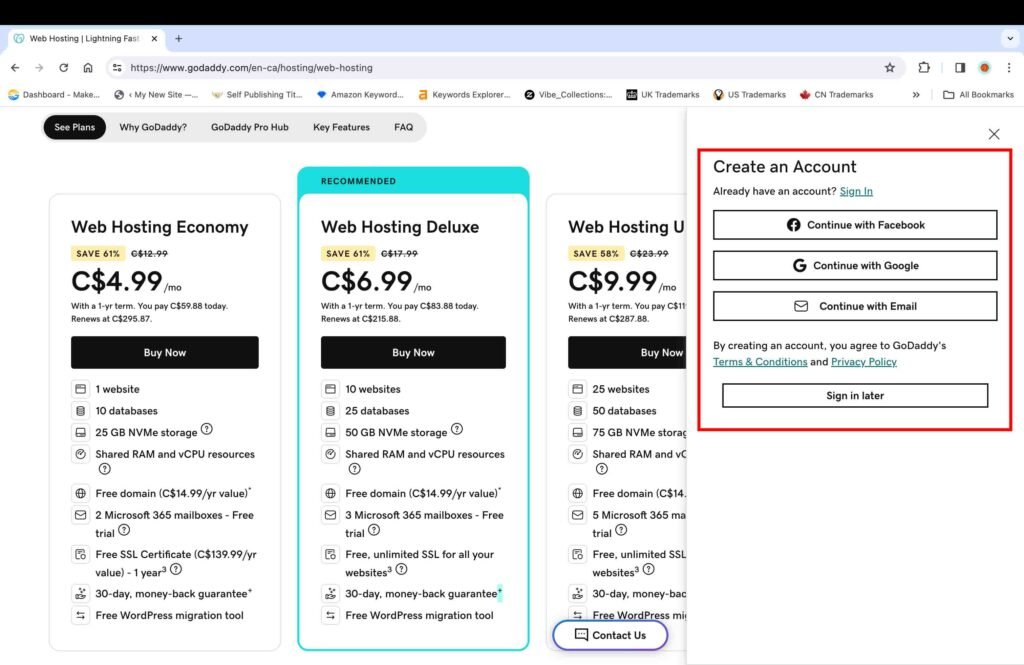
Once you create an account, you will be redirected to the payment page. On this page, you will see an add-on for the “Standard SSL” certificate added by default. It is only free for one year, and after that, it renews at a yearly price that is above $100.
- Delete the Standard SSL add-on as we are using a free SSL certificate through Cloudflare, which is discussed later on in this tutorial.
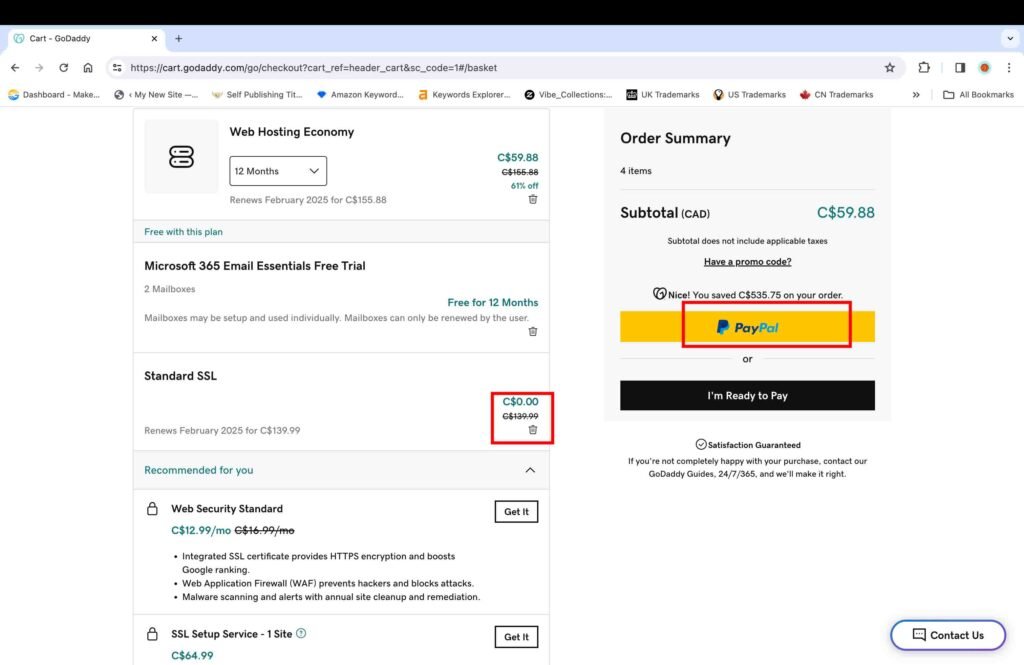
- Select the desired payment option.
- Click the “Complete Purchase” button to make the payment.
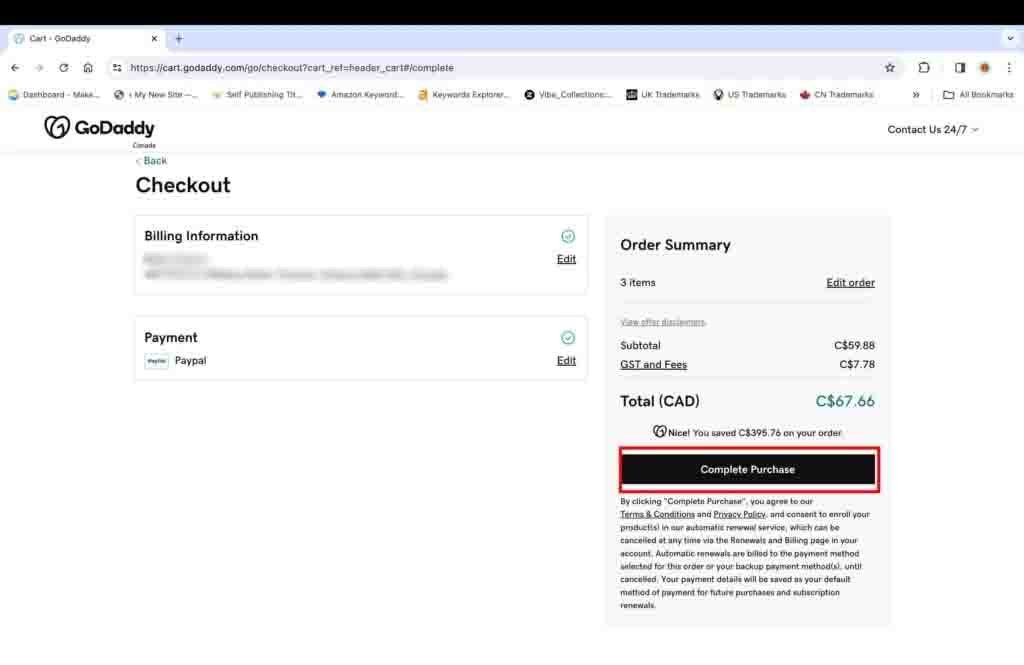
Once you make the payment, a copy of the receipt will be sent to your email ID.
- Click the “Continue” button to proceed further.
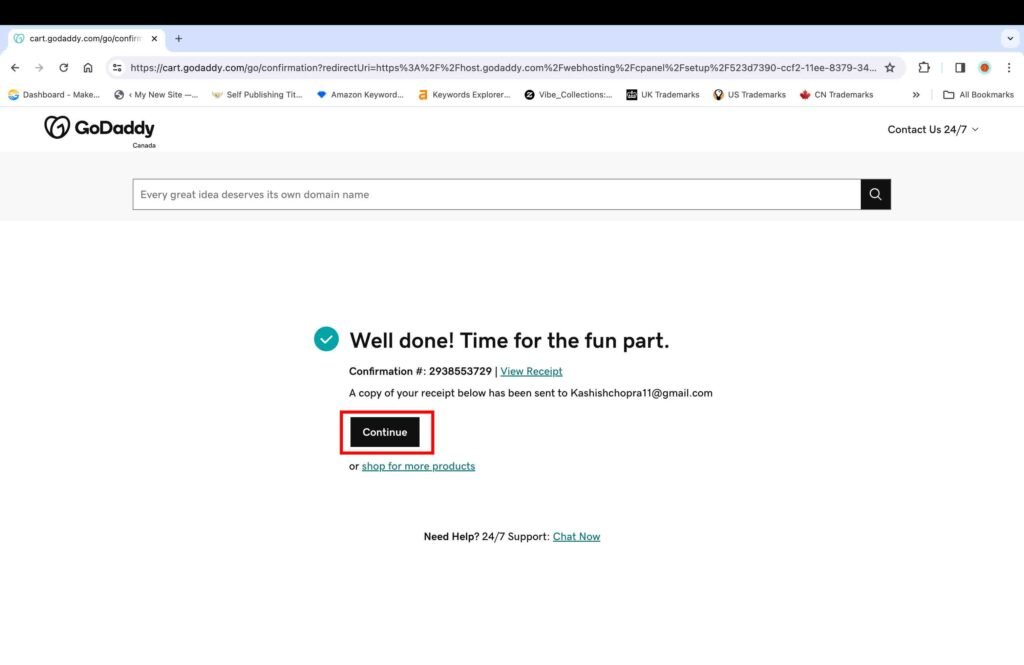
4. Set up the Website and Domain
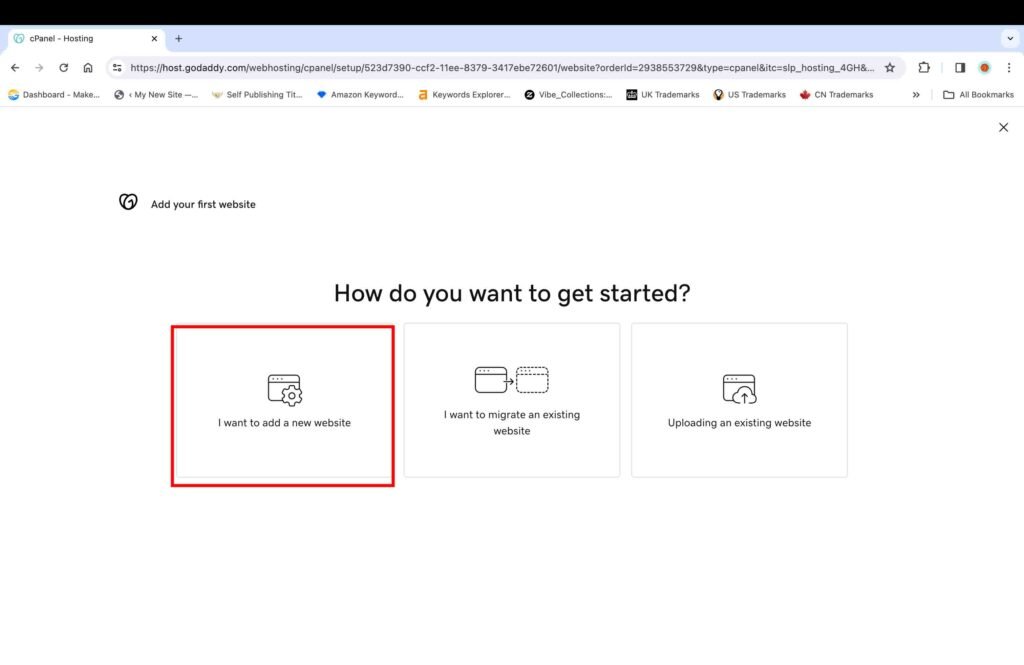
The next screen presents three options to build a website.
- Click the “I want to add a new website” option.
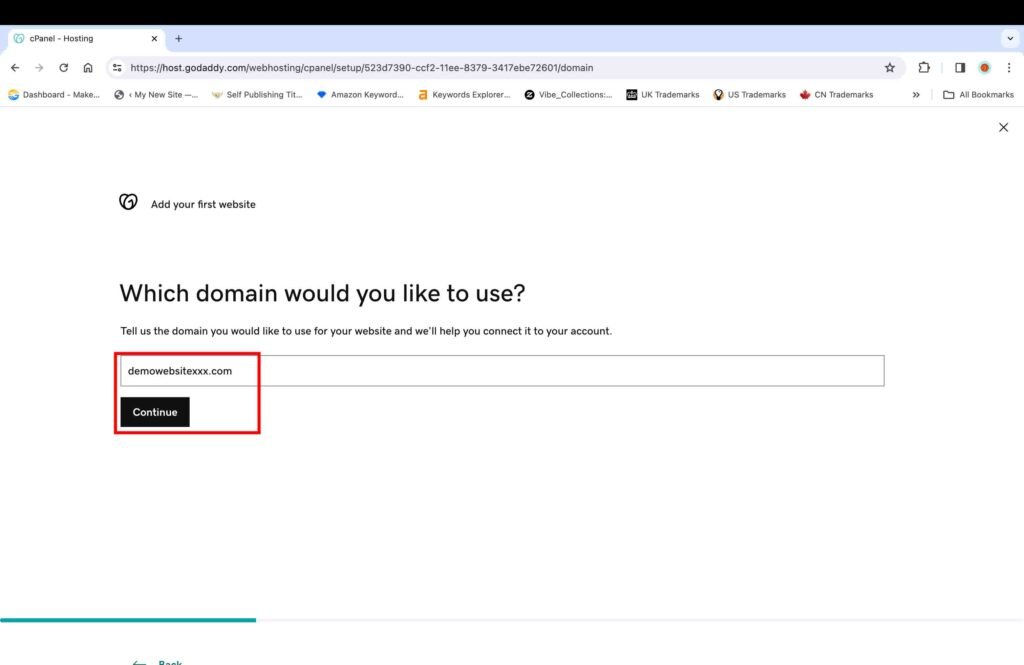
- Enter the domain name.
- Click the “Continue” button.
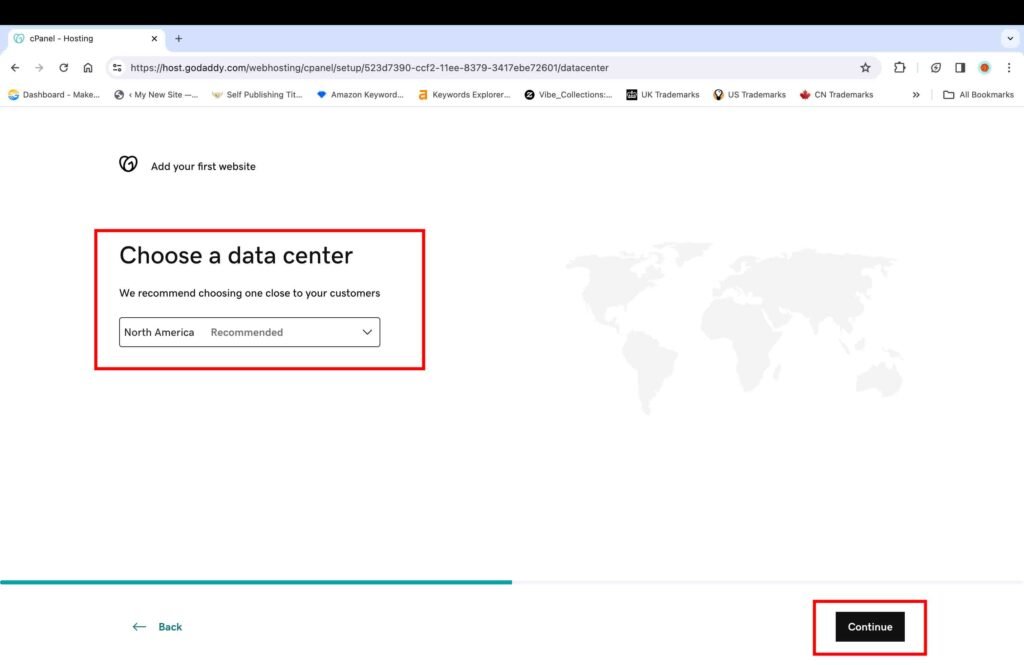
On the next screen, you will need to select the appropriate data center option.
- Select the data center location that is closest to your target audience.
- Click the “Continue” button.
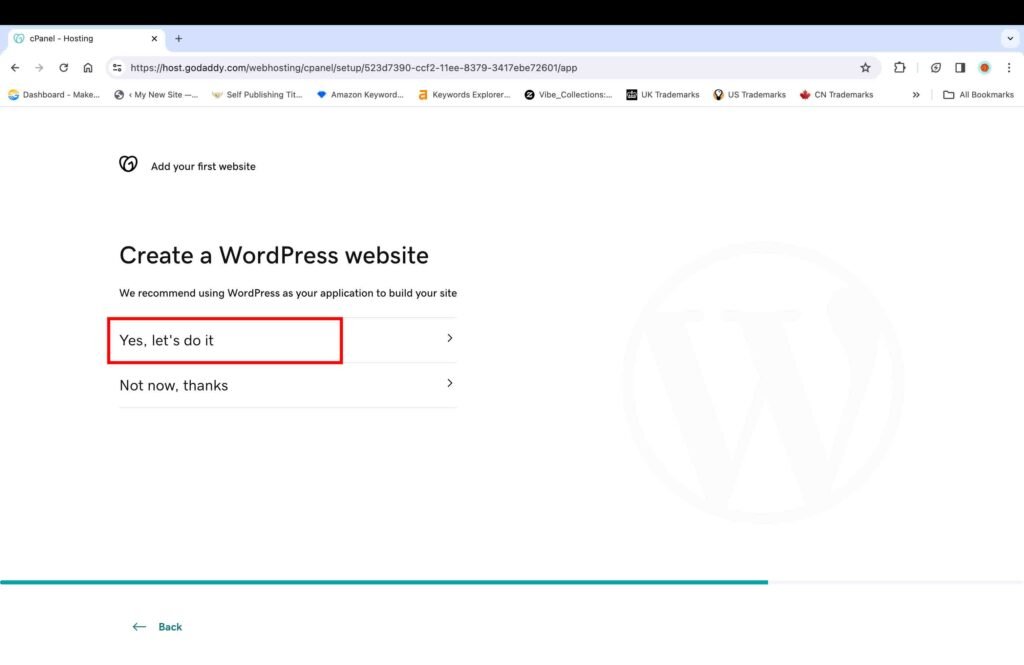
- Click the “Yes, let’s do it” button to proceed further.
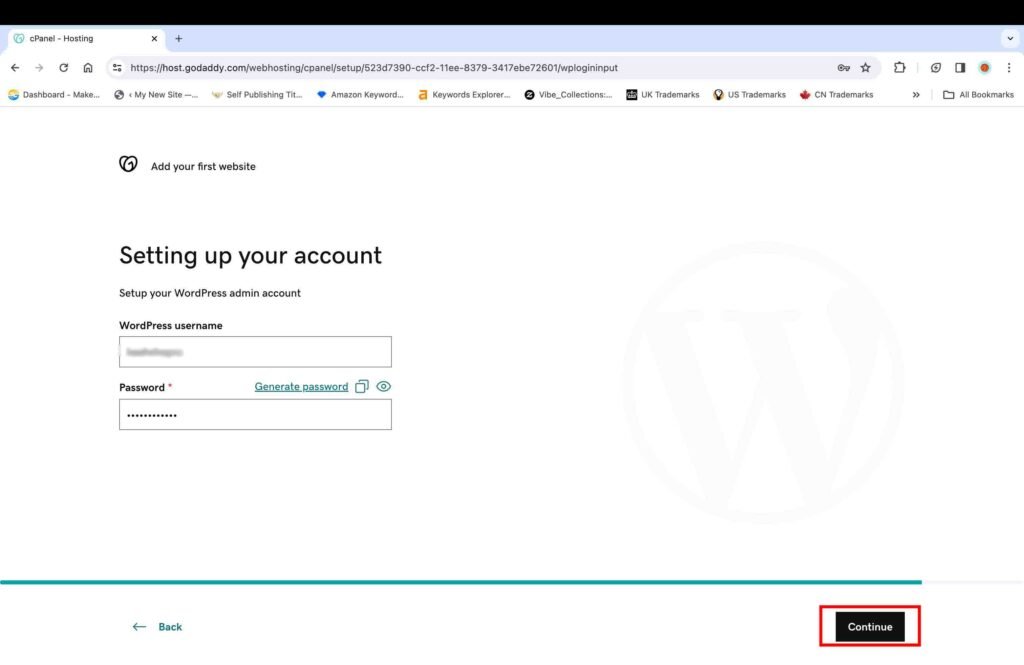
- Set your WordPress username and password.
You should always choose a strong password to make your WordPress account more secure.
5. Connect your Domain
The next screen will display the DNS records that need to be entered into the DNS records of your domain registrar. Usually, the domain registrar is the same website you purchased the domain name from. For the purpose of this tutorial, the domain name was purchased from IONOS, which is also the domain registrar. You can purchase a domain name from any website of your choice.
- Manually enter all nine displayed records into your domain registrar’s DNS records.
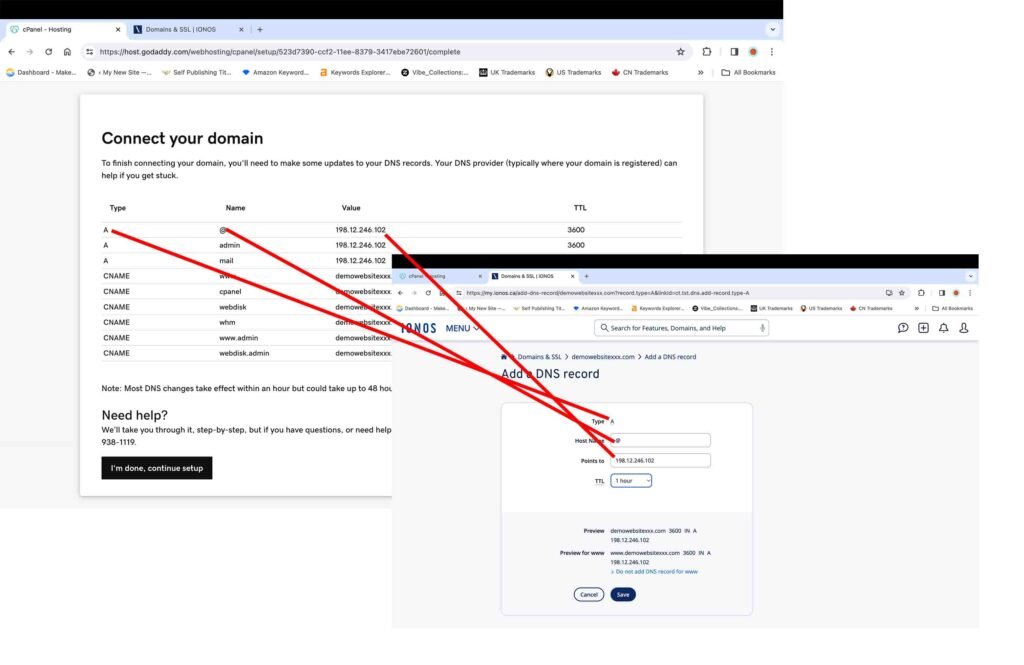
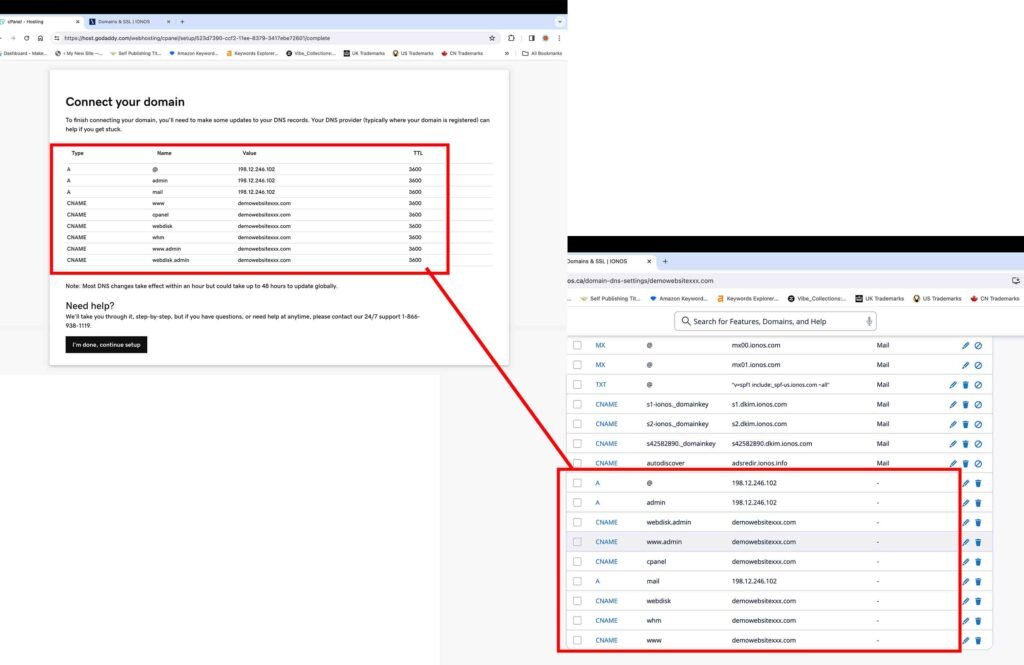
- Click the “I’m done, continue setup” button at the bottom to proceed further.
- Click the “Go to Dashboard” button.
- Click the “Admin” link to login to your WordPress admin dashboard.
6. Install a Free SSL Certificate
6A. Create a free Cloudflare Account
You can get a free SSL certificate for your WordPress website through Cloudflare.
- Click the “Sign up” button at the top of the screen to create a Cloudflare account.
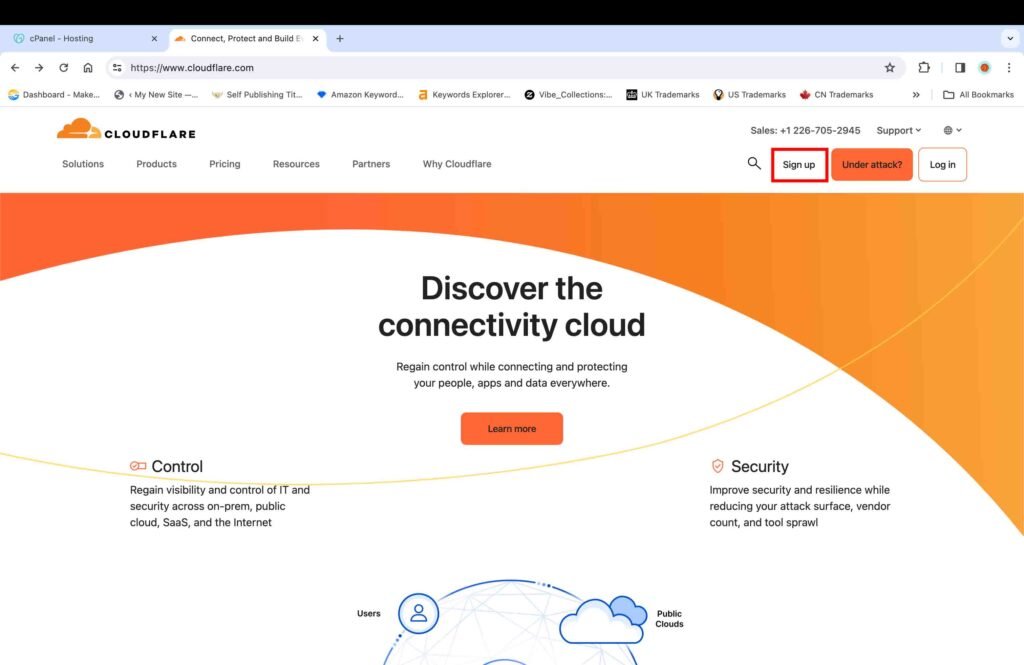
- Click the “Add a Website” button under the free plan option.
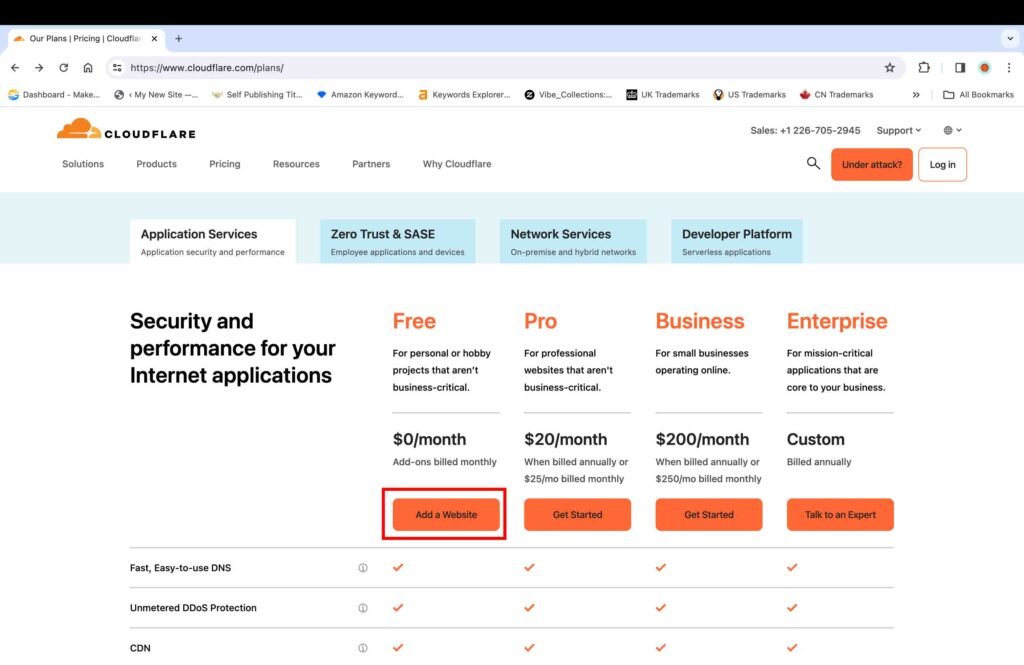
- Set the login credentials for your free account.
- Click the “Sign up” button to proceed further.
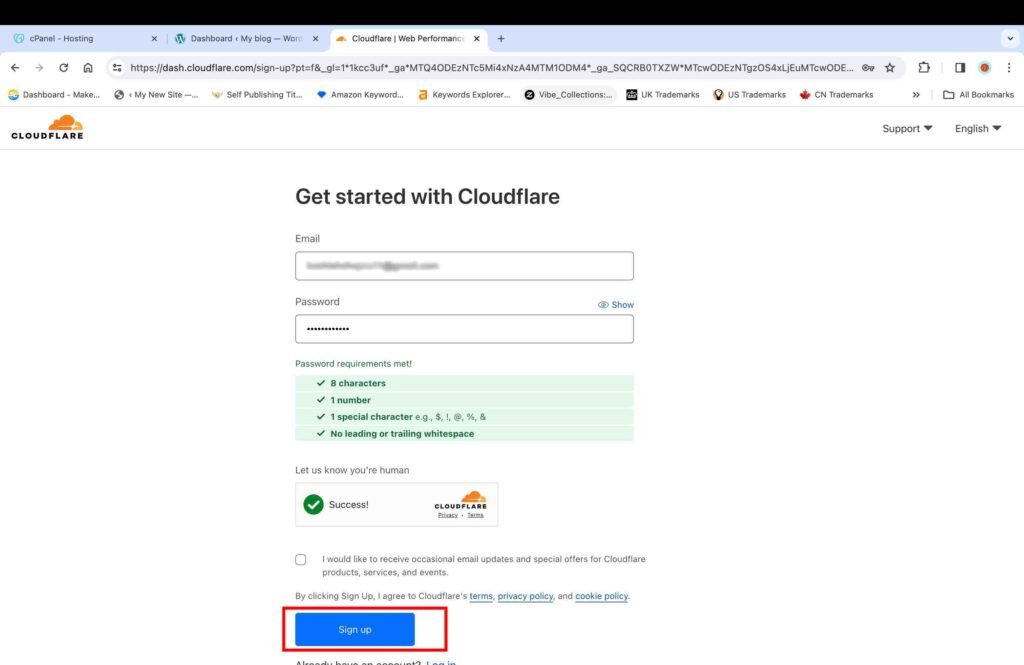
6B. Add the website to your Cloudflare account
Once you sign up for the Cloudflare account, you enter the home page.
- Click the “Get Started” button to add your website to the Cloudflare account.
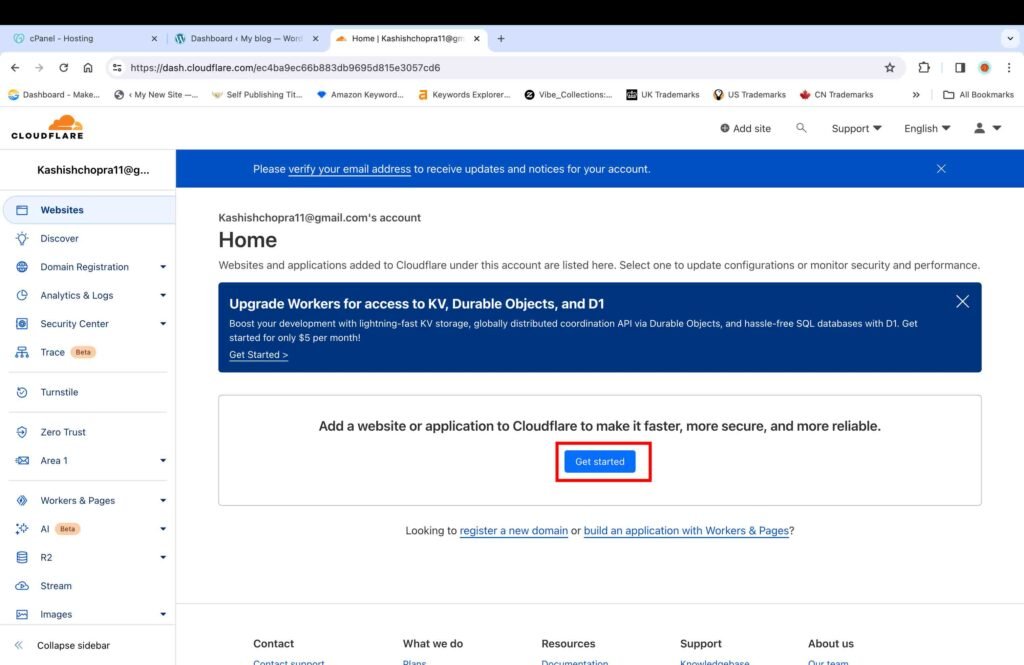
- Enter your website name in the format “website.com”
- Click “Continue.”
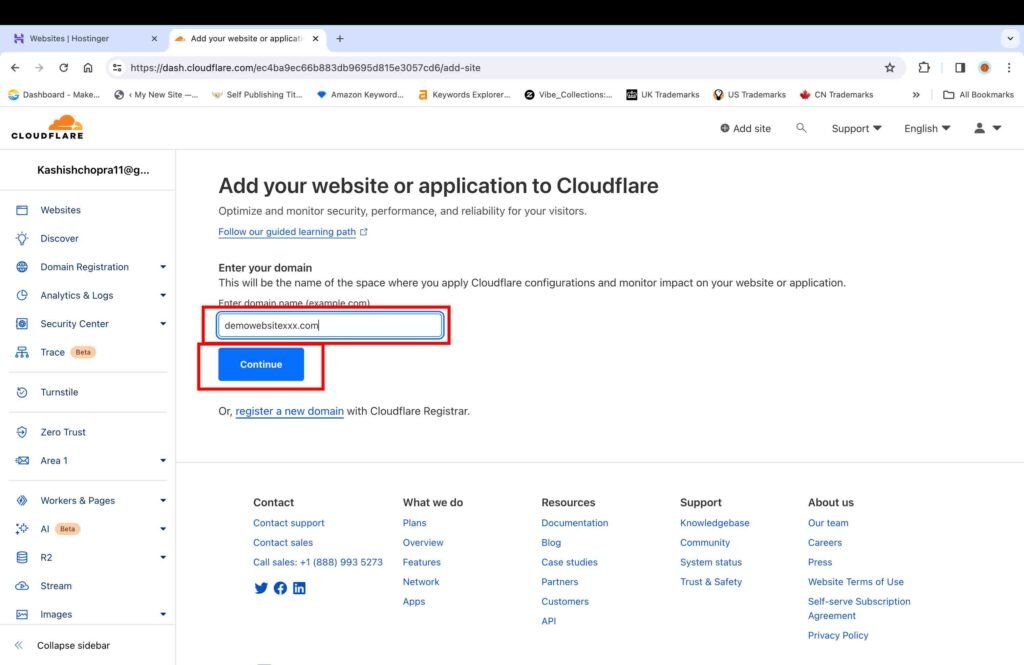
The next screen will show different paid plans and a free plan.
- Select the free plan at the bottom.
- Click “Continue” to proceed further.

Cloudflare automatically scans and imports your domain registrar’s DNS settings.
- Verify that all the DNS records have been successfully imported from the domain registrar.
- Click “Continue.”
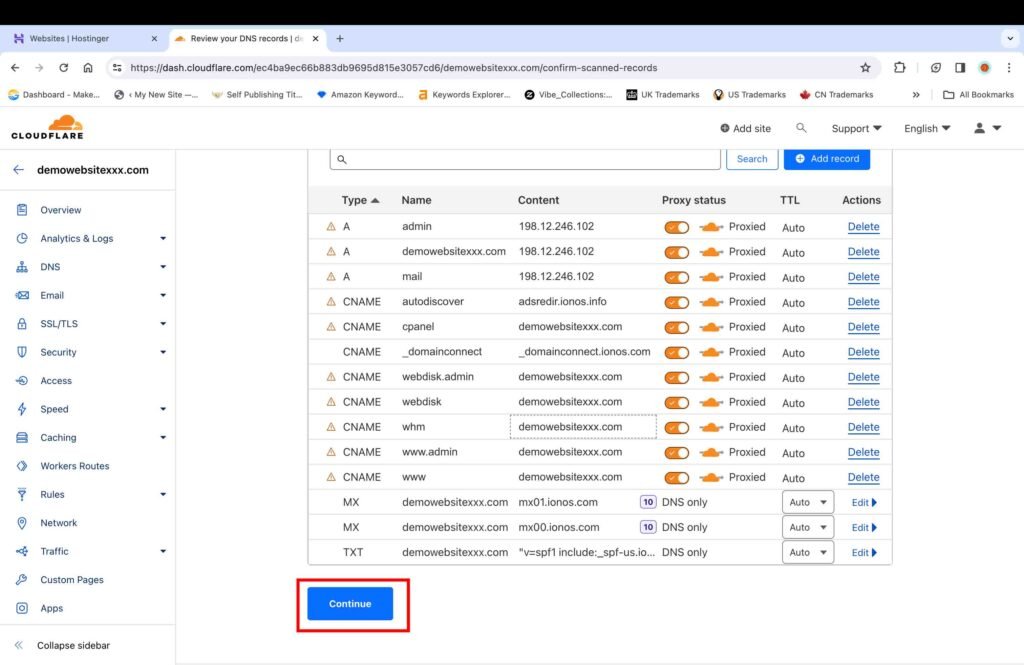
6C. Add Cloudflare Nameservers to Domain Registrar’s Records
On the next screen, you will find two Cloudflare nameservers.
- Login to your domain registrar account.
- Enter the two displayed Cloudflare nameservers into your domain registrar’s records using the custom name servers option.
For the purpose of this tutorial, the domain name provider IONOS was used. This option to use custom name servers exists at other major domain registrars as well.
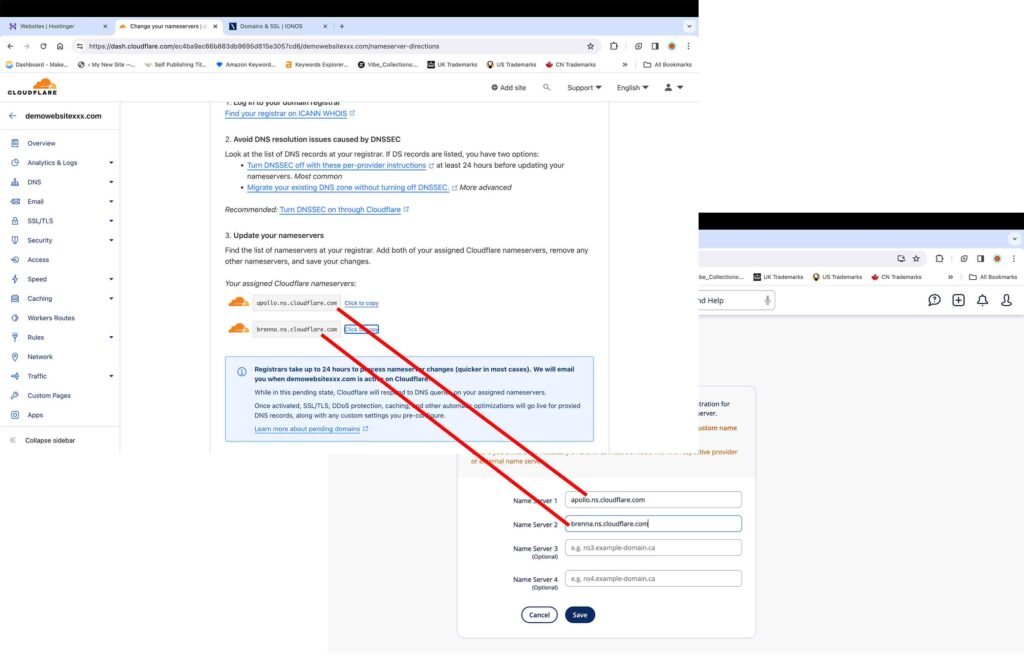
After you have saved the Cloudflare nameservers, it generally takes a few hours for the Cloudflare free SSL certificate to get activated on your site.
Once activated, you will see your website name on Cloudflare’s home page with the status “Active.”
- Click on the added website on the home page of your Cloudflare account.
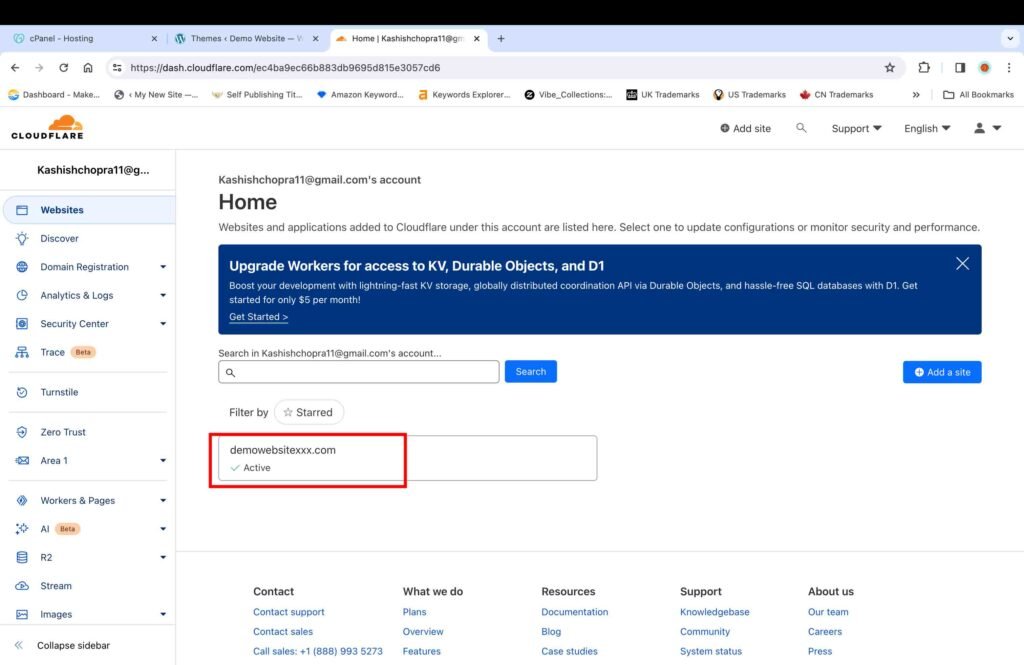
- Click the “SSL/TLS” section.
- Change the encryption mode to “Full.”
If your website still shows an error regarding the SSL certificate with this setting, you can change it to “Full (strict)” to see if it resolves the issue.
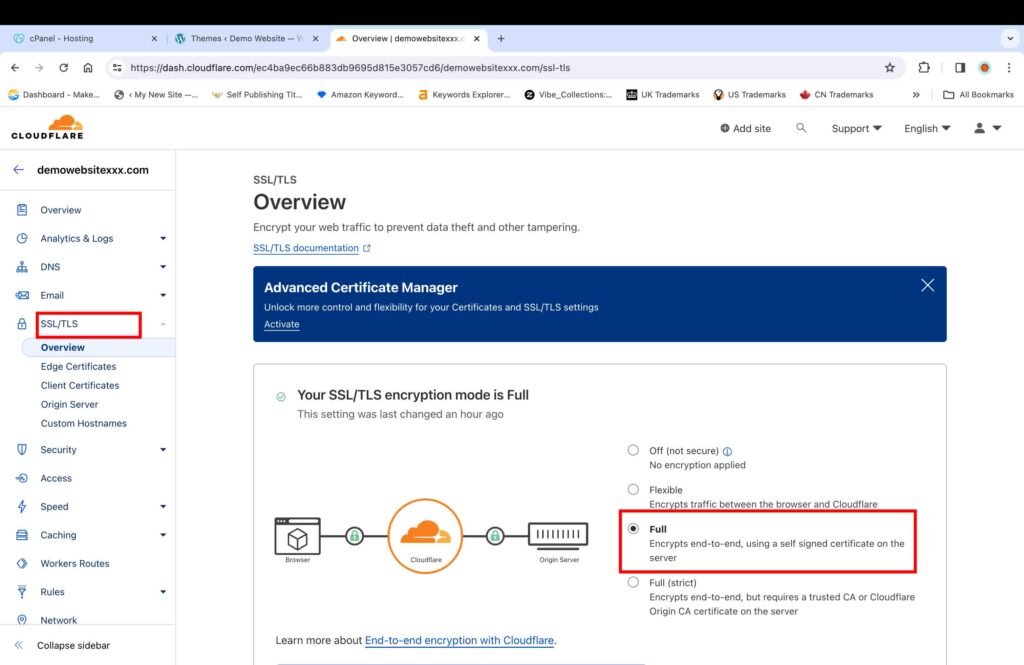
Once the Cloudflare SSL certificate is activated, the message that the website is not secure will disappear, and anybody can visit your website.
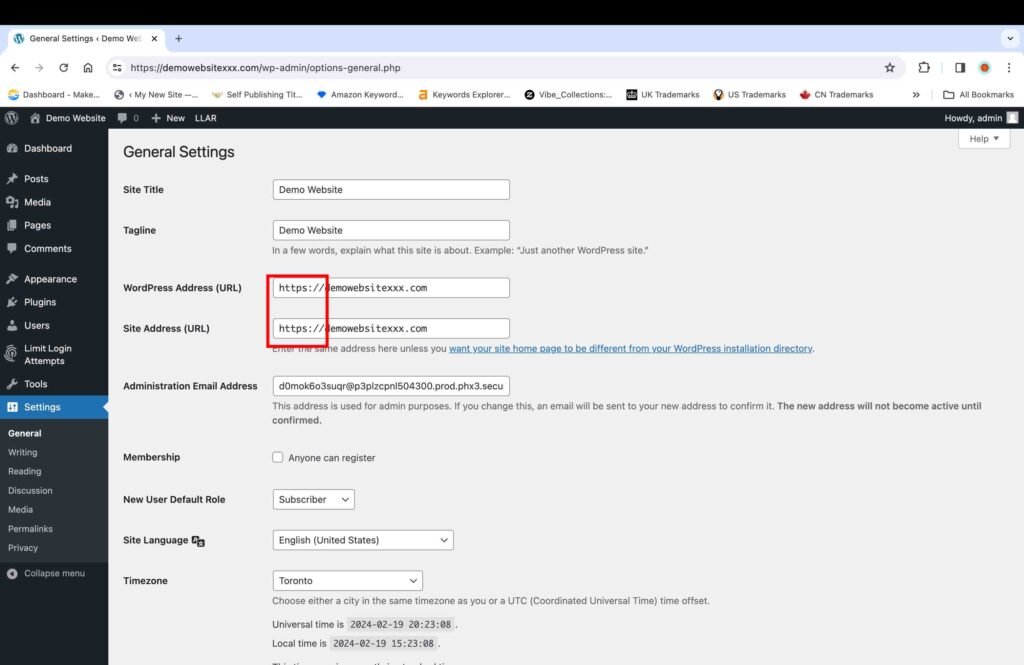
7. Update the General Settings
The next important step is to make sure that the site URL is changed from http to https.
- Go to the “General Settings” section.
- Update both the “WordPress Address (URL)” and “Site Address (URL)” from HTTP to HTTPs.
- Update the site title, tagline, and time zone.
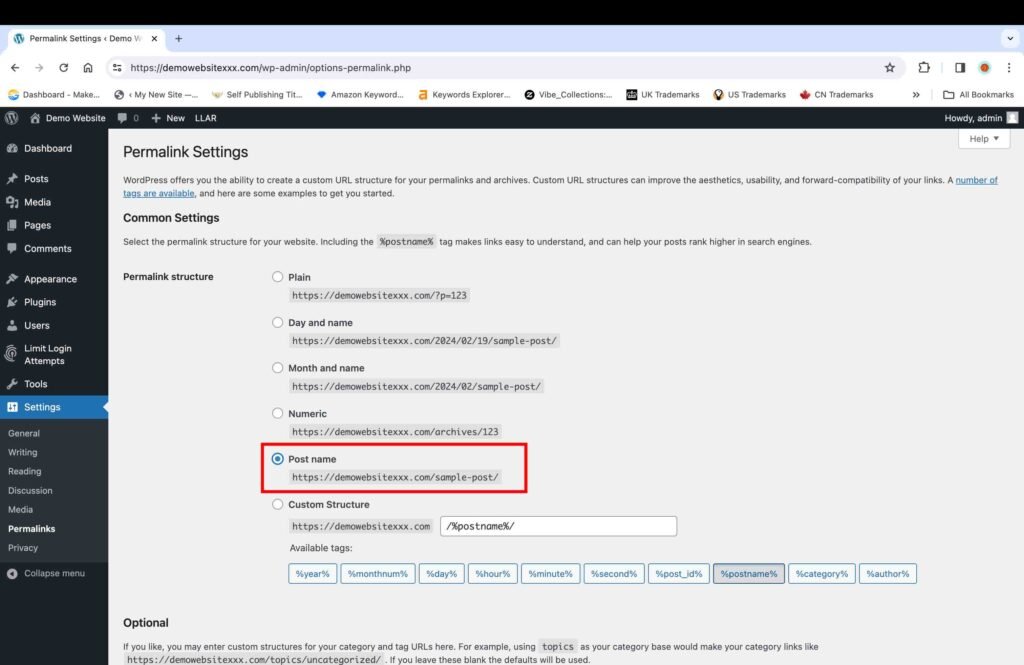
8. Set the Permalink Structure to the Post Name.
The next step is to set the Permalink structure of the blog posts to “Post Name.” This structure is considered ideal for SEO optimization and keeps the URL links simple. Selecting the appropriate permalink structure right in the beginning is very important because changing it later on, after you have already published multiple blog posts, will have a negative impact on SEO. You can read more about this in detail at Best WordPress Permalink Structure for SEO on the HubPost website.
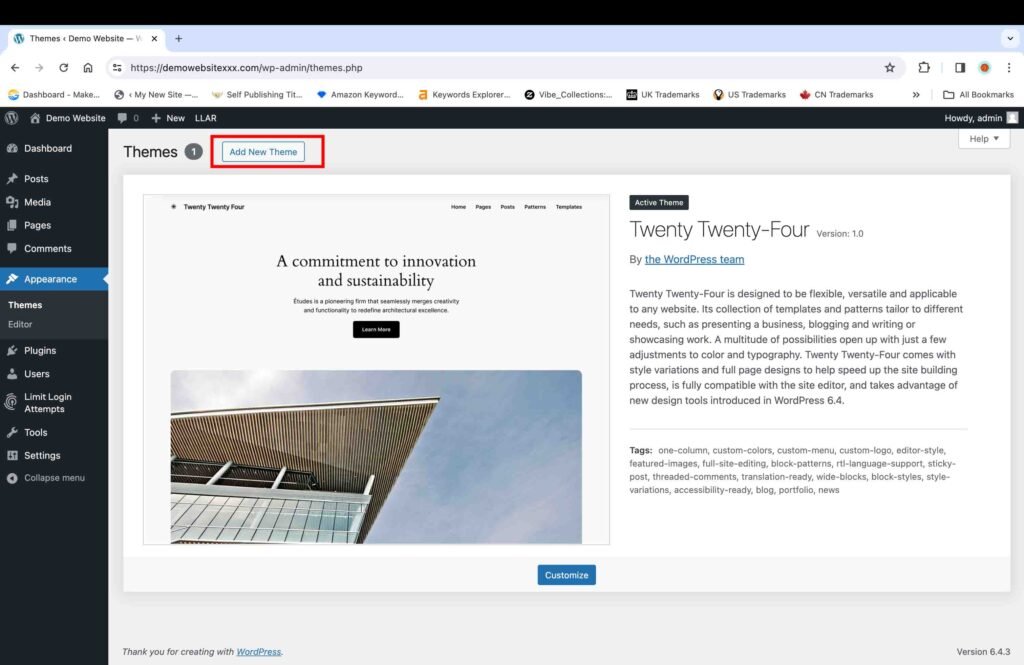
9. Install the Astra Theme
The next step is to install a WordPress theme that is safe and SEO-friendly. There is a huge library of themes available on WordPress; however, it is important to note that one should go for a theme that is safe and secure. Astra theme is one of the popular WordPress themes that is considered safe because it is frequently updated, which is very important for your website’s security when it comes to building your site on an open-source platform like WordPress. In order to install the “Astra” theme, perform the following steps:
- Go to “Themes” under the “Appearance” section.
- Click on “Add New Theme.”
- Search for the term “Astra.”
- Hover over the Astra theme that appears in the search result.
- Click on “Install.”
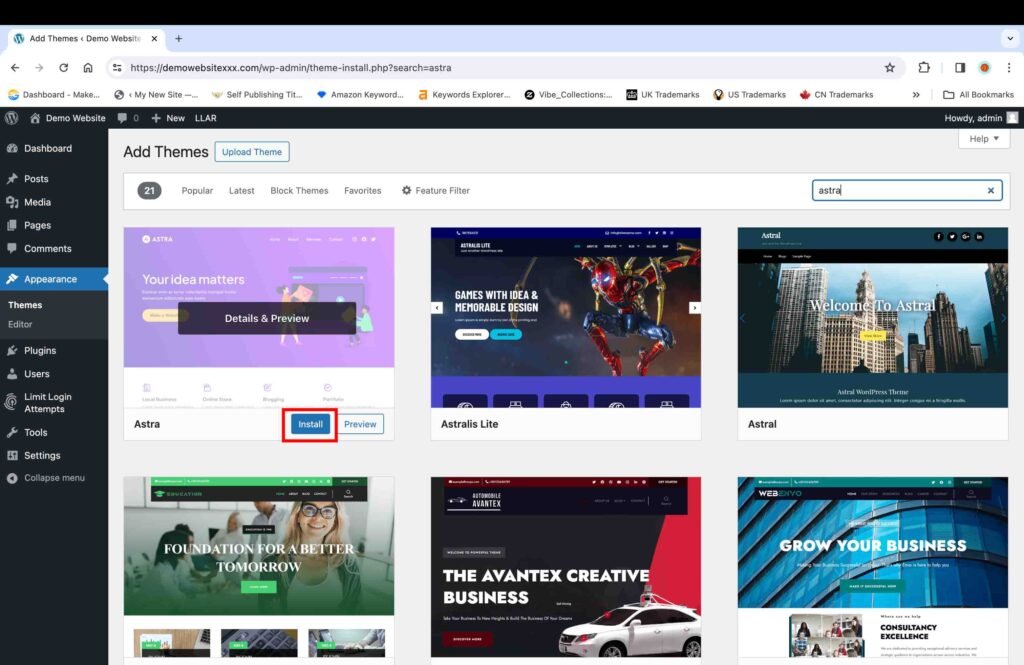
Once the theme is installed, you will see the “Activate” button.
- Click the “Activate” button to launch the theme.
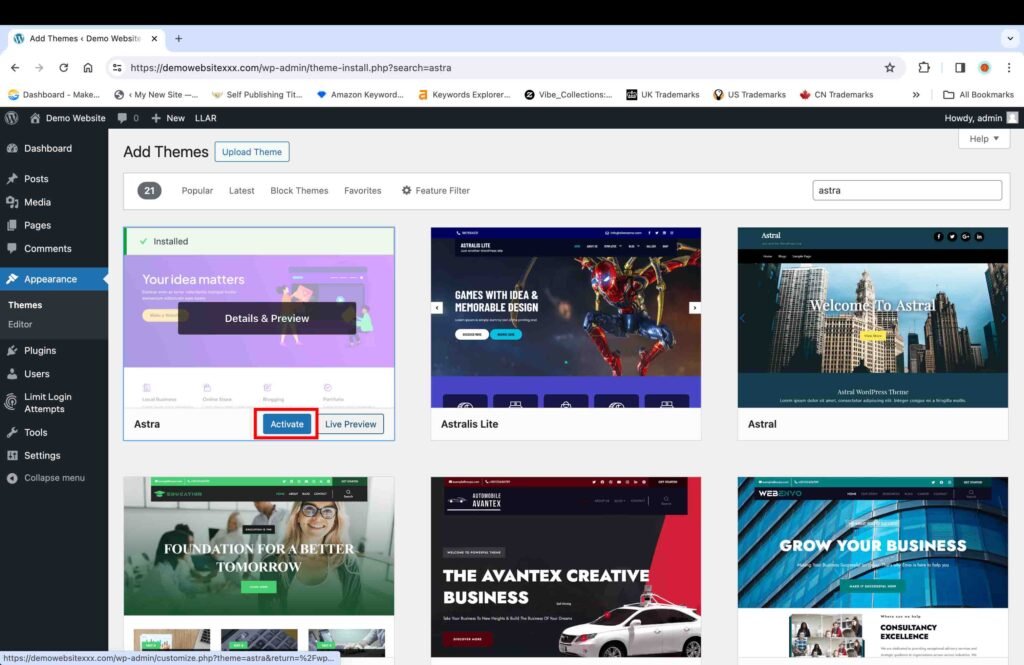
I0. Install Starter Templates
Astra Theme offers a wide range of templates to suit various business needs through a plugin called “Starter Templates.” When the theme is activated, you will be automatically redirected back to the “Themes” page under the “Appearance” section.
- Click the “Install Starter Templates” button on the banner at the top of the “Themes” page.
Alternatively, you can also install the starter template plugin by searching for it in the “Plugins” section.
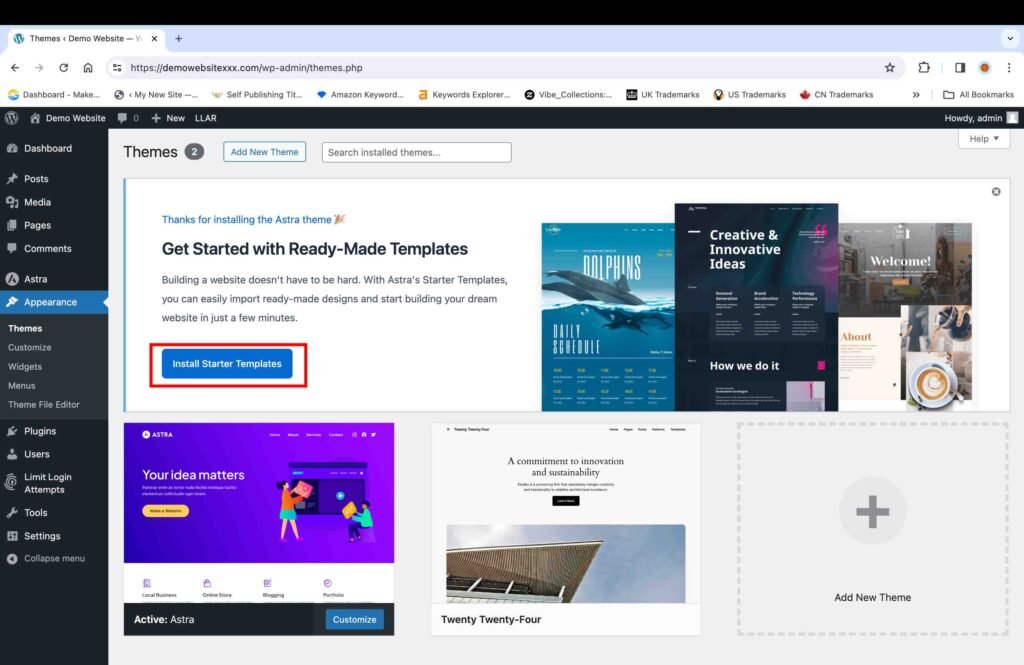
11. Build the Website
Once you click on the Starter Templates under the “Appearance” menu item, you will enter the screen that will present two options to build the website: Classic Starter Templates and AI Website Builder. We will opt for the Classic Starter templates because it is comparatively easy to build a website with ready-to-use templates that can be tailored with minimal effort to meet your website’s needs.
- Click the “Build with templates” option.

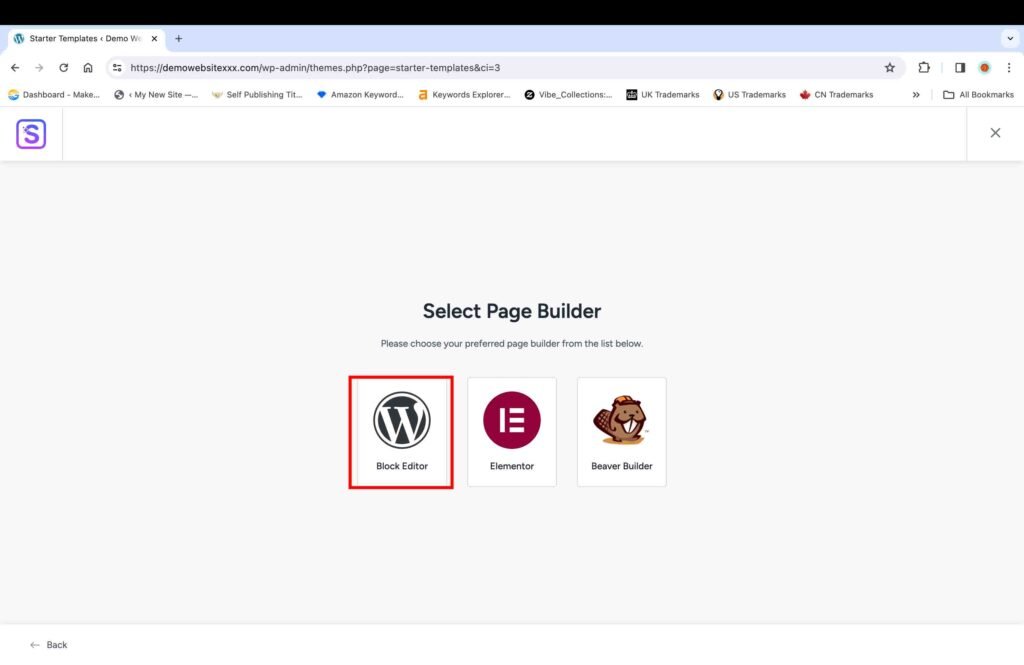
The next screen will present three page builder options.
Click the “WordPress Block Editor” option to build the website.
On the next screen, you will enter the “Starter Templates” library, which offers a wide array of both free and paid templates to suit various website needs. The templates are broadly classified into business, local business, personal care, professionals, personal sites, community, e-commerce, and blog categories. You can select the template that best meets your website’s purpose. For the purpose of this tutorial, the free template “Mountains” was chosen.
12. Customize the Template
Once you click on the desired template, you will be taken to the customization pages.
- Upload your website logo, if any. If you don’t have a logo, you can skip this step and delete the default logo image later on using the “Customize” tool.
- Click the “Continue” button.
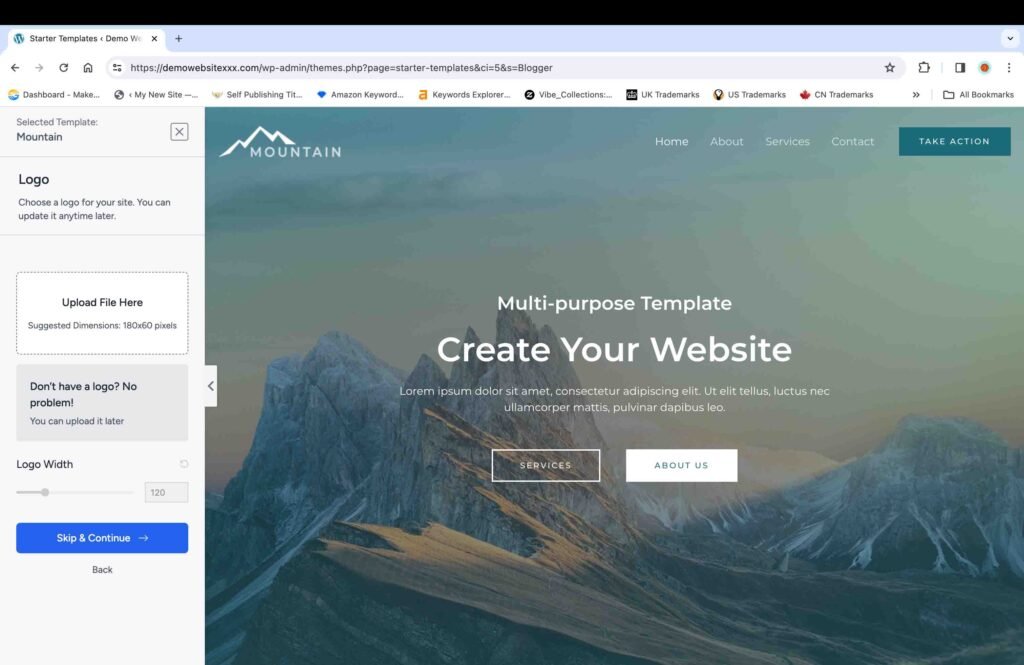
On the next screen:
- Select the default colors and fonts for your website.
- Click the “Continue” button.
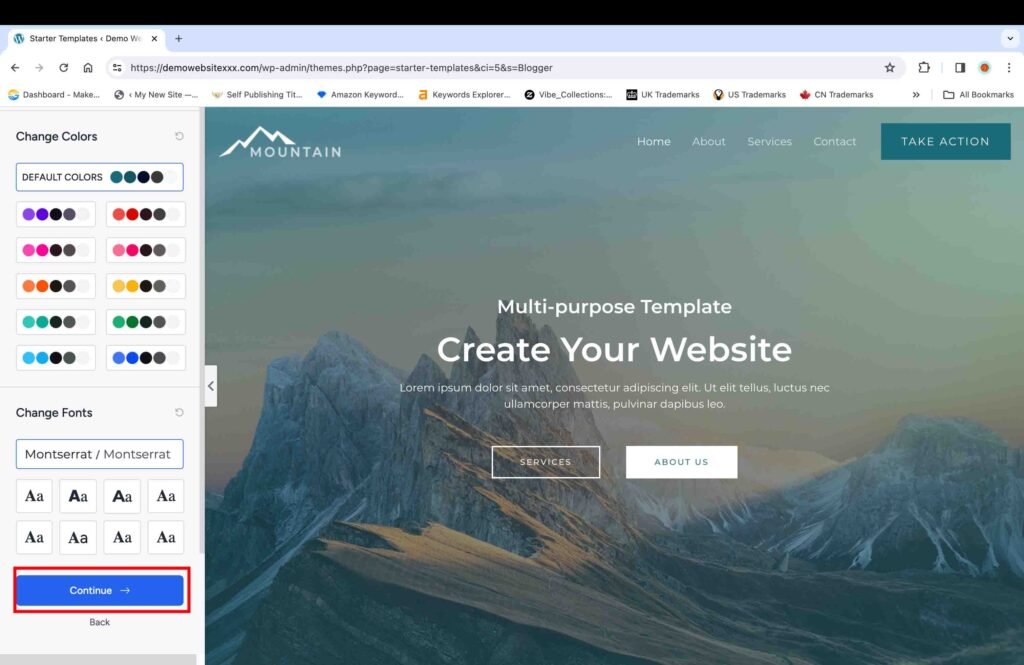
On the next screen, you can submit your website. All the advanced options are checked by default. However, make sure that the first four advanced options are checked in any case. The last option relating to sharing non-sensitive website data is optional and depends on your personal choice.
- Click the “Submit and Build My Website” button.
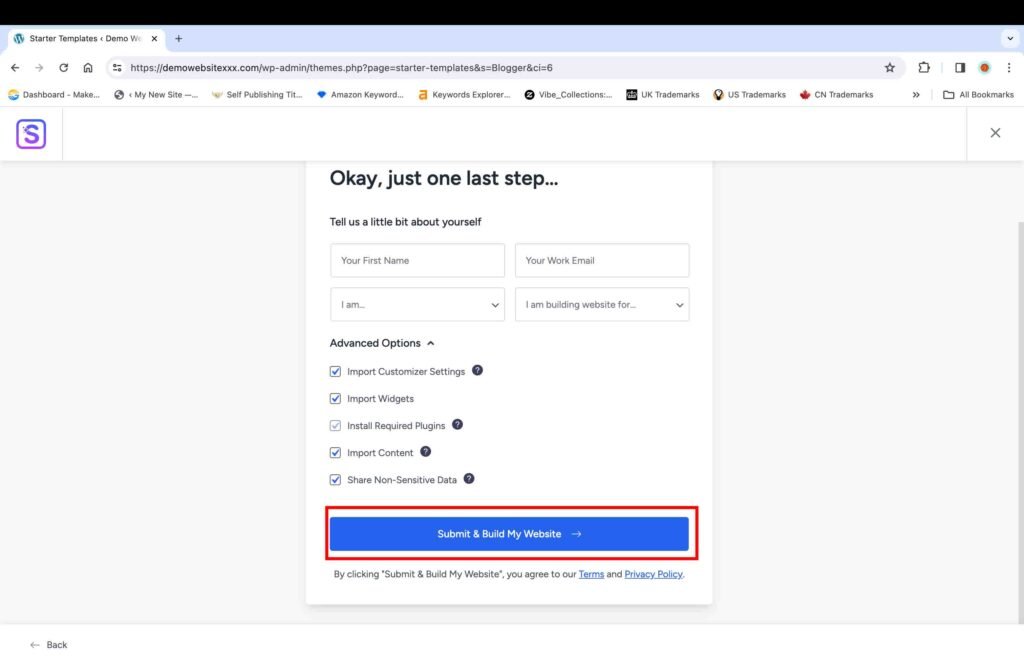
It generally takes a few seconds for the website to be ready.
- Click on the “View my Website” button to enter your website.
13. Tailor the Website
You only need two tools to tailor your website:
- Edit Page tool
- Customize tool
The “Customize” tool lets you customize the fonts, headers, footers, and more. You can also add custom CSS codes with this tool.
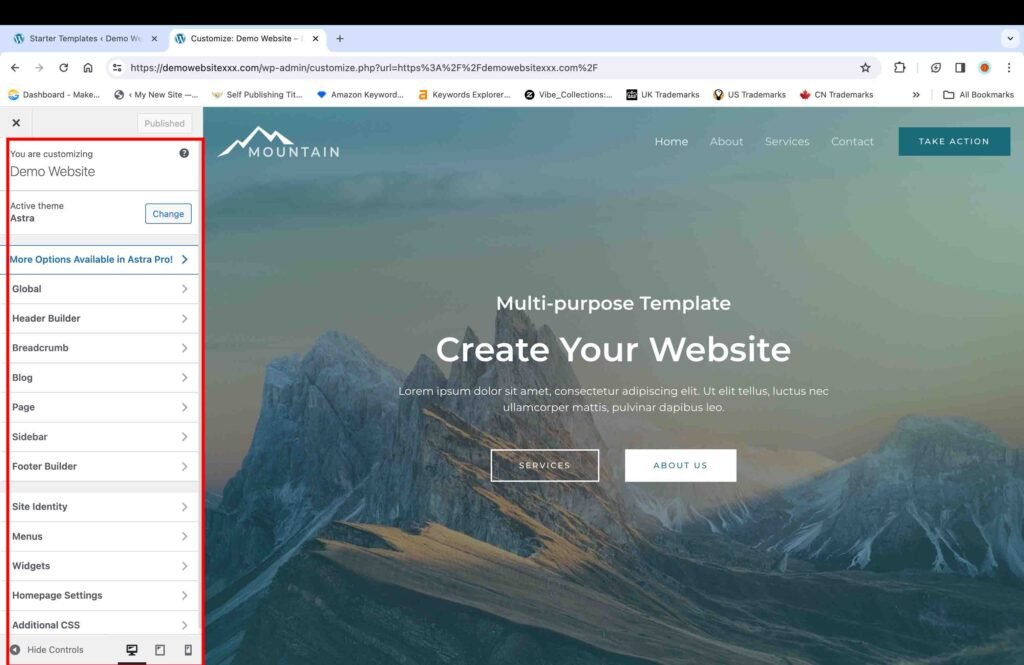
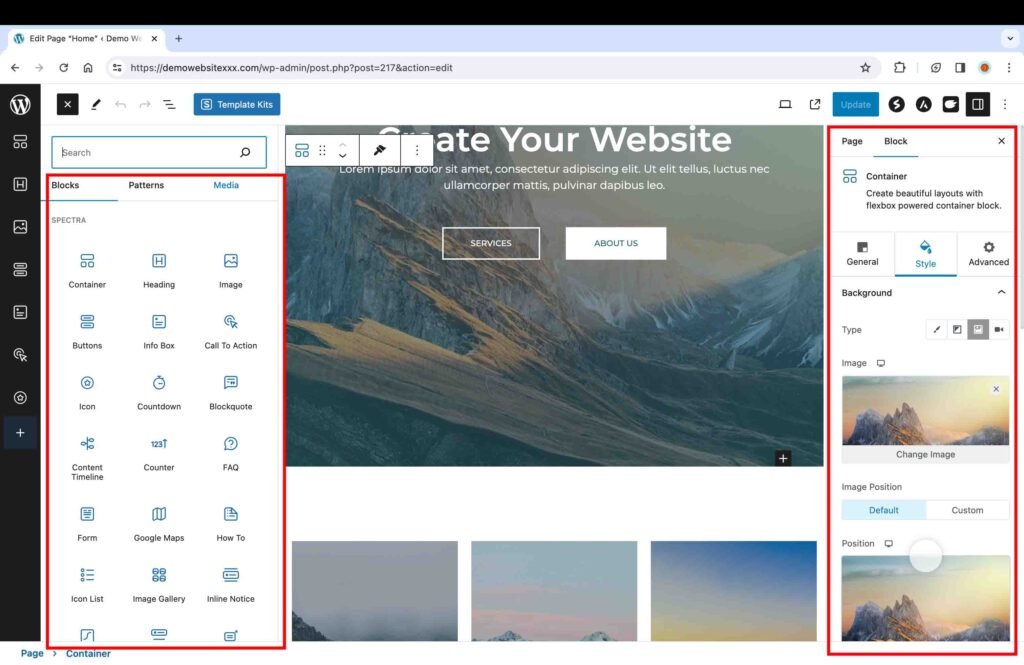
The “Edit Page” tool lets you add different types of content, such as containers, text, forms, buttons, images, and more, to a specific page.
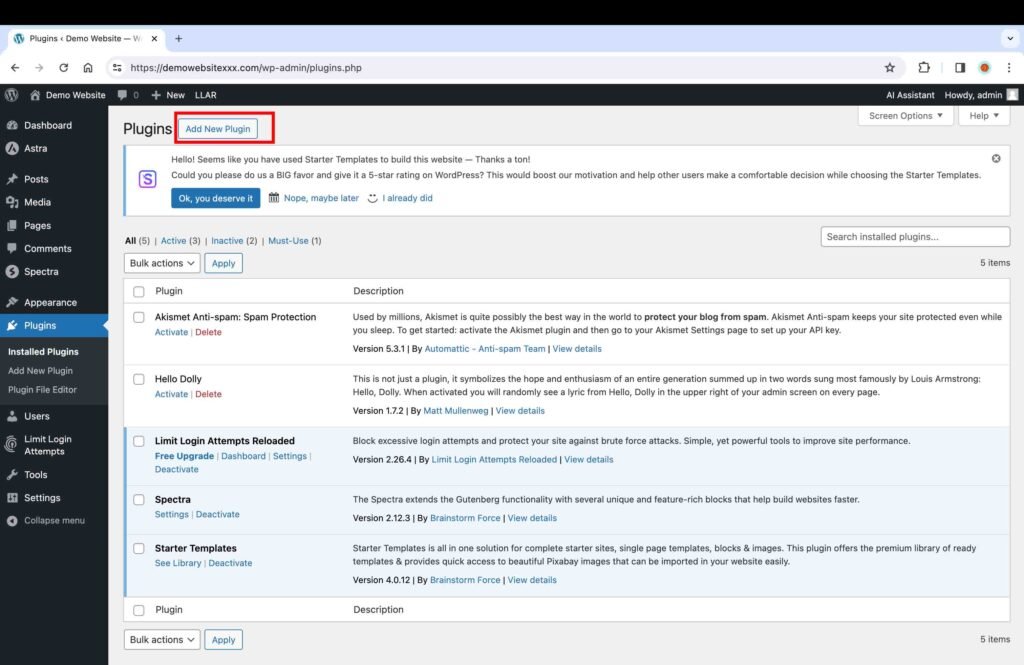
14. Install the Necessary Plugins
Plugins are free or paid software programs that offer security and customization features for your WordPress website. These plugins save a lot of time and money because anyone can install them to meet their security and customization needs without the need to code or hire someone to perform the task. For example, there are security plugins to enhance a website’s security against cyberattacks, hacking, etc. Additionally, there are various plugins that can add contact forms to your WordPress website. There are thousands of plugins out there for various needs. Furthermore, these programs can be installed within the WordPress dashboard at the click of a button. In order to install any plugin, perform the following steps:
- Search for the plugin’s name.
- Go to the “Plugins” section.
- Click the “Add New Plugin” button.
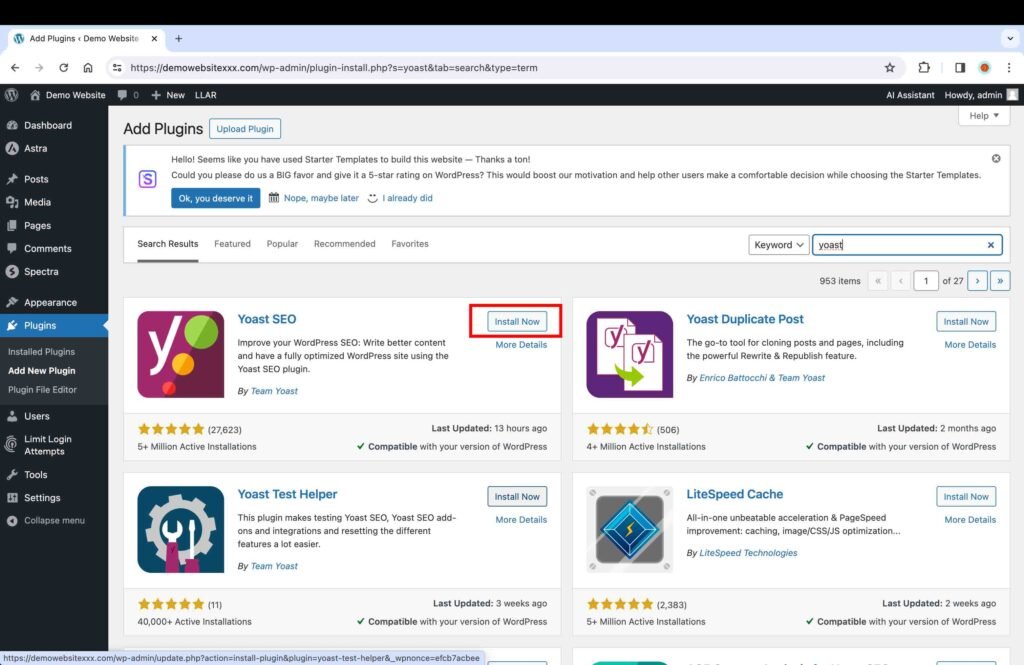
For instance, if you are installing the Yoast SEO plugin, type in the term “Yoast” in the search bar on the “Add Plugins” page.
- Click the “Install Now” button to install the plugin.
Once a plugin is installed, the “Activate” button will appear.
- Click the “Activate” button to activate the plugin. Alternatively, you can also activate the plugin on the “Installed Plugins” page.
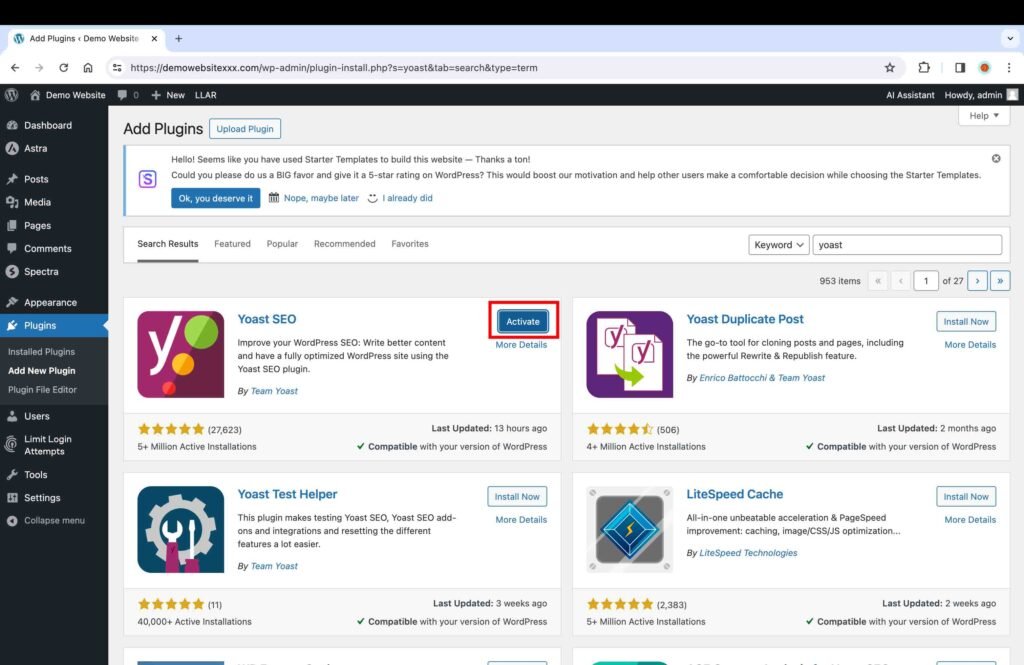
Recommended Plugins:
- Yoast SEO provides SEO optimization suggestions for a blog post and web page.
- Wordfence Security provides protection against hacks and malware.
- UpdraftPlus provides security backups at any defined frequency.
- Really Simple SSL provides enhanced security for a website.
- LiteSpeed Cache provides page caching for enhanced site performance.
- WPForms Lite provides a drag-and-drop form builder.
- Enable auto-updates for all plugins in order to save time spent updating a plugin manually whenever an update is available.
15. Disable Certain Content
From an SEO perspective, certain content needs to be disabled to avoid thin and duplicate content issues in the Google search results. You can accomplish this with the help of the Yoast SEO settings page.
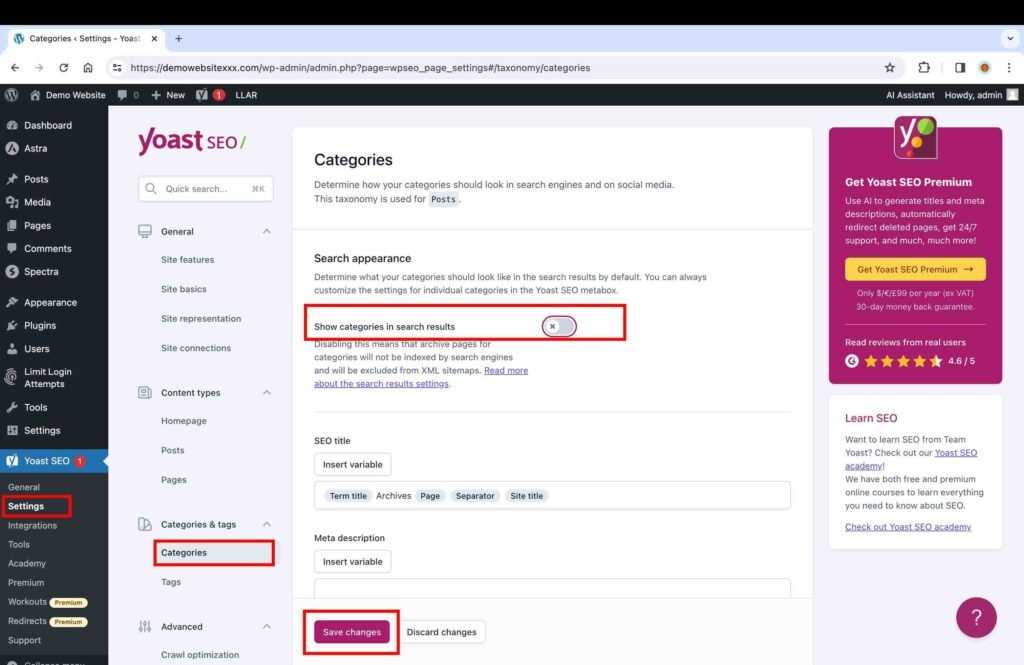
Categories
Categories are used to classify blog posts and products. For instance, a blog writing articles on website development can publish articles related to hosting, website builders, website design, and so on. In this case, hosting, website builders, and website design are categories. Before a blog post is published, you need to assign a category to it. After a blog post is published, two pages will be created: a blog post page and a category page containing that blog post’s excerpt with the link to the original blog post page itself.
Why Categories should not be indexed?
Generally, a category page contains thin and duplicate content because it usually contains excerpts of original blog posts related to that category. Therefore, if category pages are not critical for your audience, you should disable them so that they are excluded from the Google search results. This prevents spamming the search results with duplicate and thin content. While it is not clear whether these pages have any negative or positive impact on SEO, I would stay away from them so that they don’t become an issue in the future. However, these pages can be useful in some cases. For instance, they can be quite useful for an e-commerce website when you want your audience to land on a page that displays similar products in a particular category.
It is worth noting that if you do want to keep these pages indexed for whatever reason, it will require careful strategy and continuous monitoring over time to make sure that they are not competing with the main content pages or negatively impacting your website’s SEO in any way. I found a very insightful article on the WSI Wavery Digital website that clearly explains why category pages should be set to no index. The article is titled Why Tags, Author Archives, and Categories on WordPress Sites Should Be Set to Noindex: An SEO Perspective.
- Toggle off the “Show categories in search results” setting.
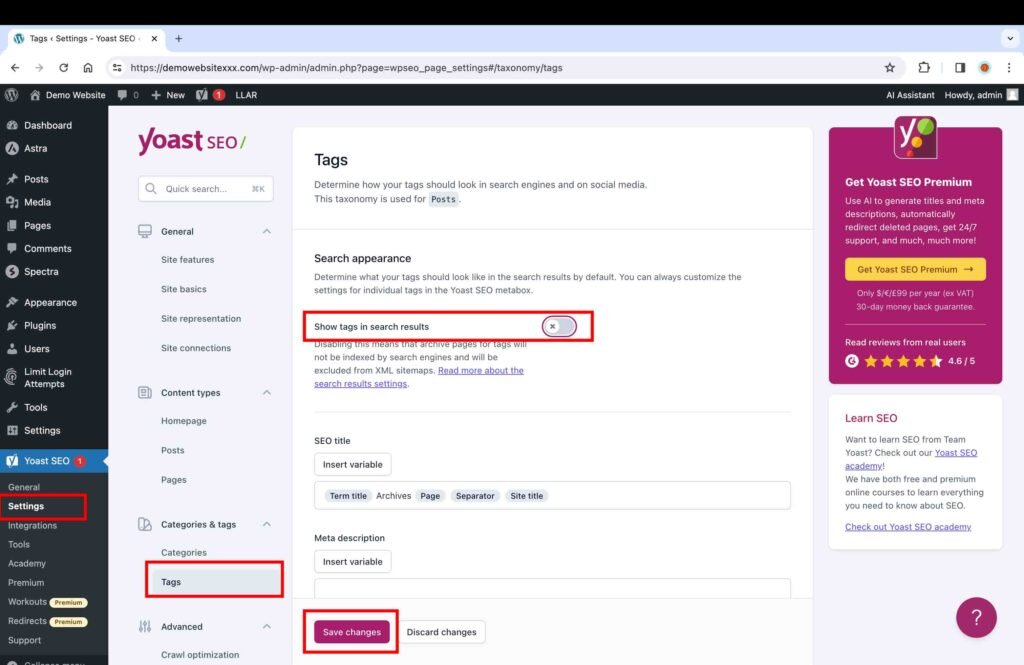
Tags
Tags are keywords that are added to a product page or blog post. These tags are used to help website owners with the organization of website content. It also helps website users find relevant information or products in the search results. A WordPress website creates a new page for every tag added to a post. For instance, if you add five tags to a blog post, five additional tag pages will be created in addition to the main blog post page. A tag page lists all posts that have used that particular tag. There is a common misconception about how tags work. These tags are not relevant for the Google search but rather for the internal search on a website. These tags don’t work like “instagram tags.”
These tag pages are usually thin in content because they only contain excerpts of blog posts with links to the original blog posts respectively. You should use these tags only if they are necessary for your website; for instance, in the case of an e-commerce store, these tags can be quite useful for site visitors searching for specific products. You can gain more insights into this topic in the article “Why you should stop using tags?” on the Yoast website.
- Toggle off the “Show tags in search results” setting.
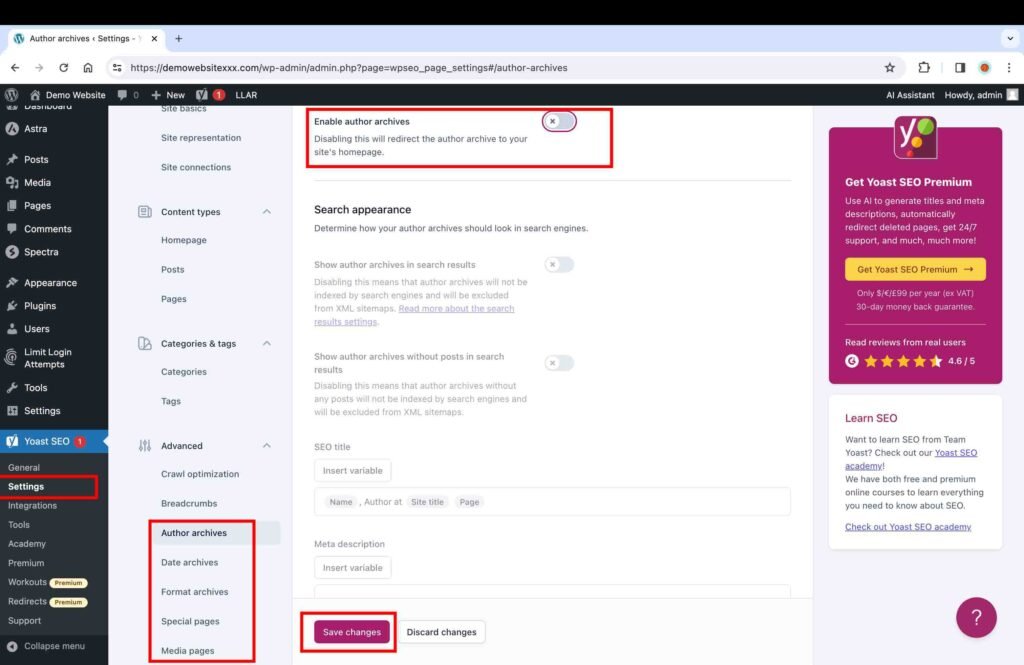
Archives and Media Pages
The next step is to disable the following content to avoid duplicate and thin content issues in the search results. You can toggle off them entirely or their search appearance.
- Author archives
- Format archives
- Date archives
- Media pages
16. Add, Edit, or Delete Pages
Apart from the home page, a website might need other pages, such as a contact page, a privacy policy page, a terms and conditions page, etc. You can add any number of pages to your WordPress website in the “Pages” section.
- To edit an existing page, click the edit option under the relevant page.
- To delete an existing page, click the trash option under the relevant page.
- To add a new page, click the “Add New Page” button at the top.
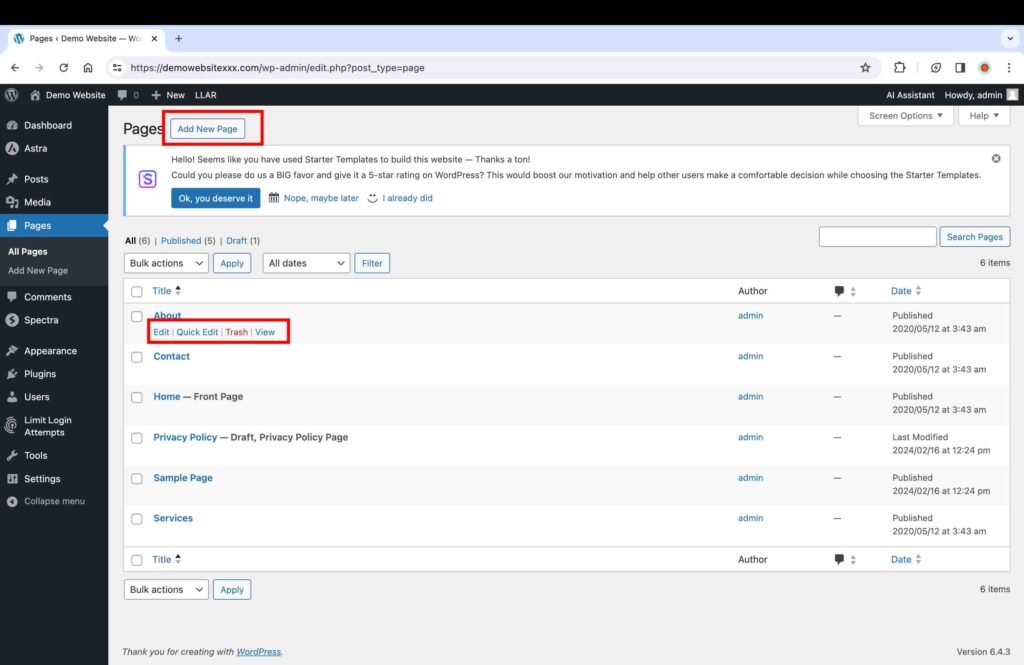
Once you click the “Add New Page” button, you will be directed to the page where you can add the content.
- Format the contents of a page using the “Block” tool dashboard on the right.
- Click the “Publish” button to publish the post.
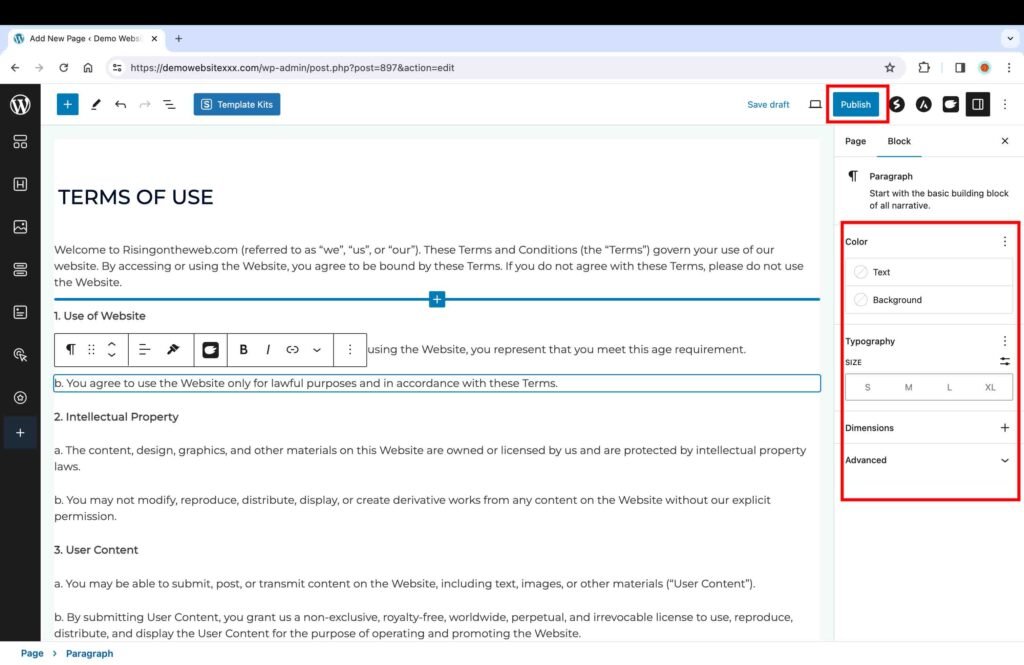
17. Add and Customize Menus
A menu can be defined as different pages grouped together that can be inserted in the header and footer of a website. You can also easily customize and create any number of menus for your WordPress website. Usually, a website always needs a header menu and a footer menu. To customize an existing menu or create a new menu:
- Go to the “Menus” page located under the “Appearance” menu item of the dashboard.
Adding a Menu:
- Click the “create a new menu” option at the top of the “Menus” page.
Customizing a Menu:
- Select the menu you want to customize from the drop-down list.
- You can update the name in the “Menu Name” text field.
- To add page(s) to a menu, select the page(s), click the “Add to Menu” button. If the page you are looking to add is not on the list in the “Pages” box, you can always create it in the “Pages” section.
- To remove a page from the menu, click on the page under the menu, then click remove, and hit save.
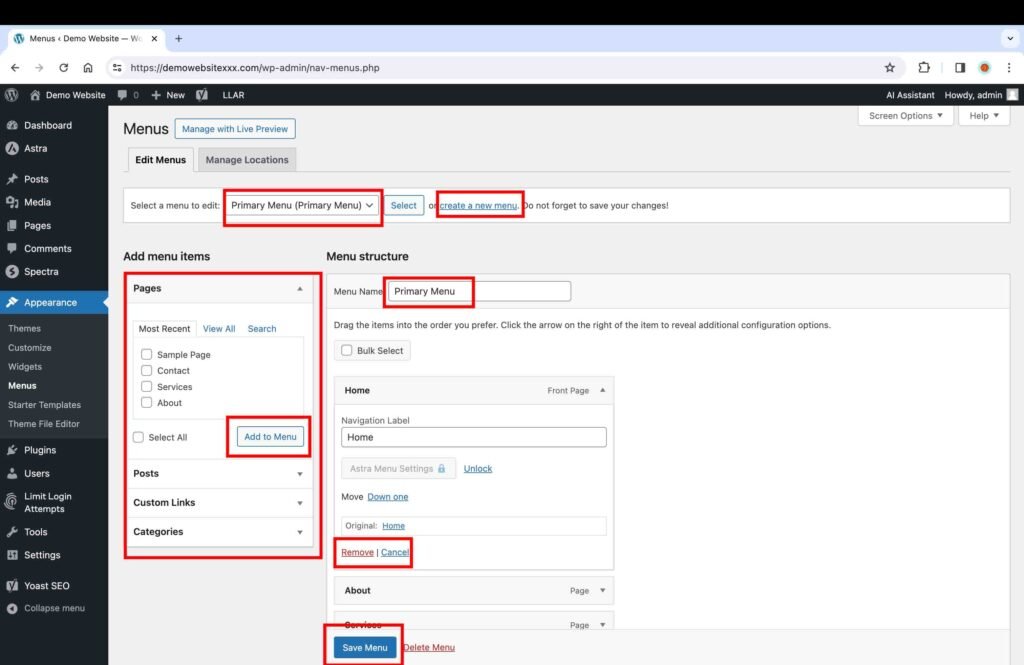
18. Make the Website Images Responsive
You will need to add custom CSS code to make your website images suitable for viewing on mobile and tablet devices.
- Click the “Customize” button.
- Click the “Additional CSS” button.
- Add the following custom CSS code:
img {
max-width:100% !important;
height:auto !important;}
}
- Click the “Publish” button to save the changes.
19. Check the Website for Different Views
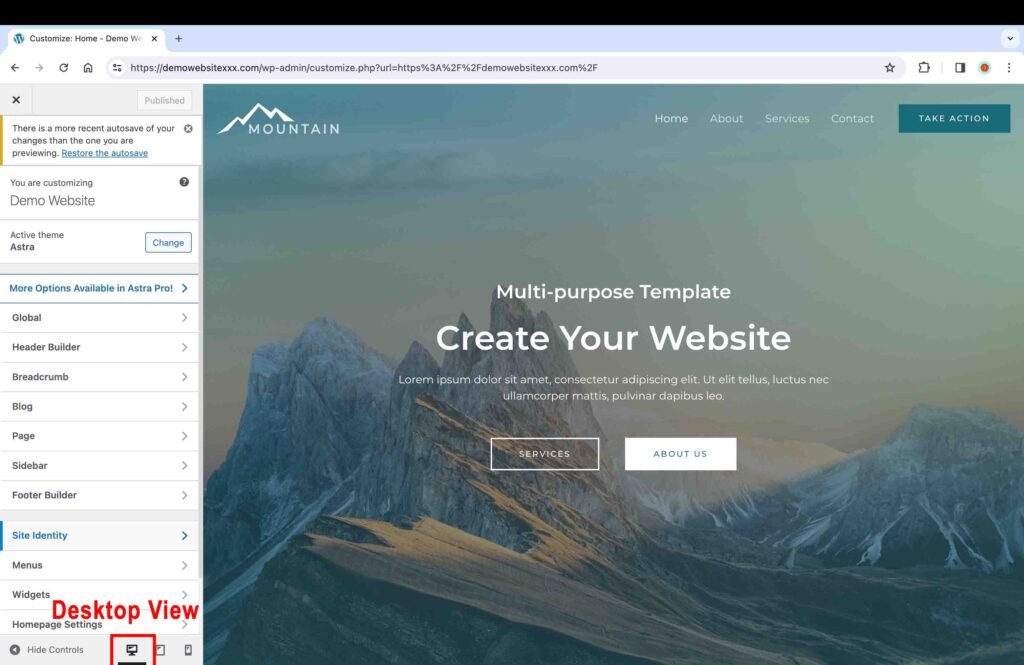
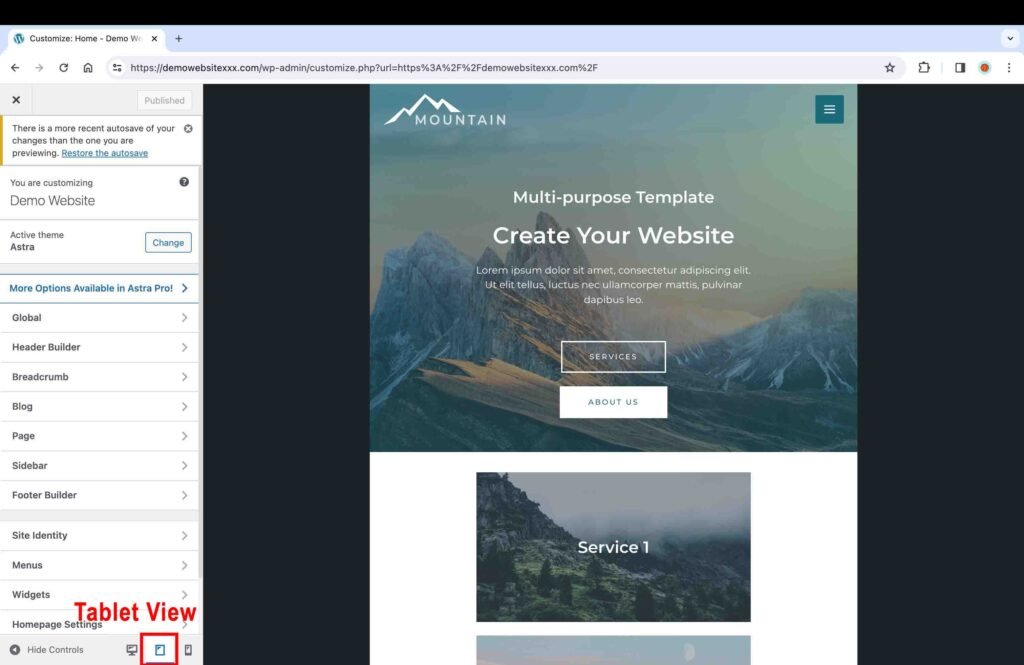
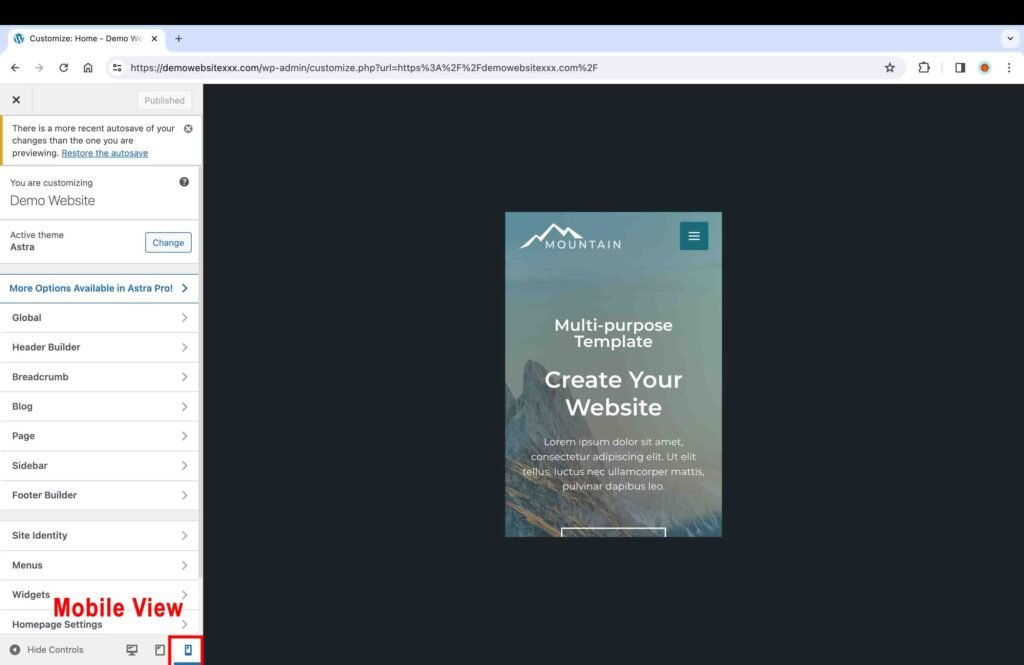
At the bottom of the “Customize” tool bar, there are three icons: desktop, tablet, and mobile.
- Click on each view to make sure that it looks good on all devices. Furthermore, you can also physically check the website on your mobile and tablet devices as well.
20. Add a Blog Post
After you have finished tailoring your website, the next thing is to start publishing content.
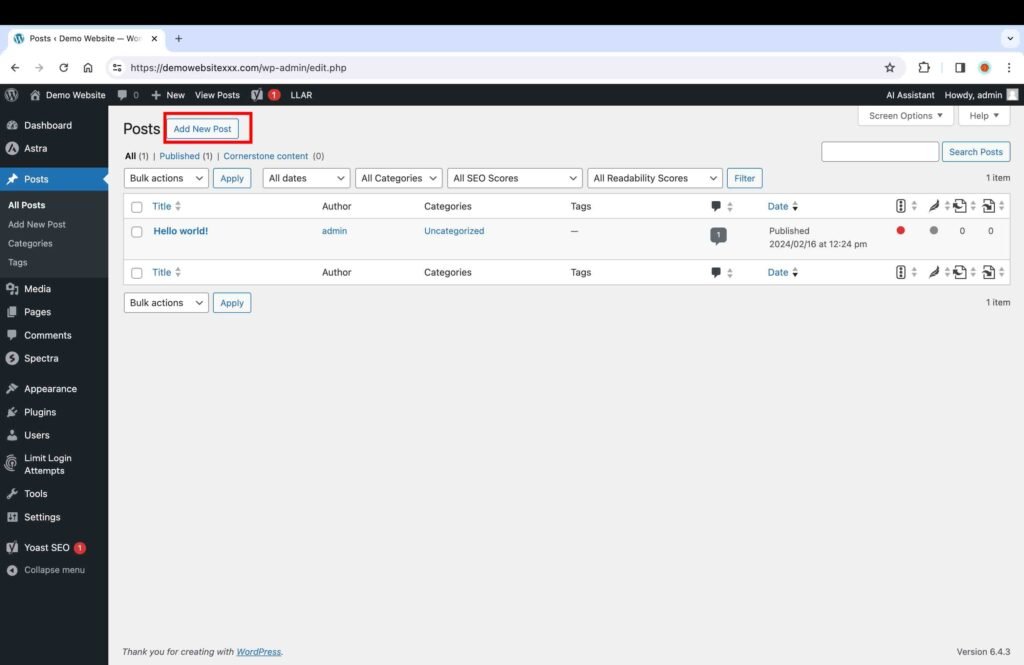
- Go to the “Post” page.
- Click the “Add New Post” button.
- Add the content.
- Use the plus icon to add paragraphs, headings, and a variety of other elements, such as images, videos, tables, etc.
- Format the content using the “Block” toolbar on the right.
- Click on the “Publish” button to publish your blog post.
Finally, you are all set with your new WordPress website with GoDaddy Hosting.
Written by Kash C. The writer is a website developer and graphic designer.